Reverse Nodes in Even Length Groups
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given the head of a linked list.
The nodes in the linked list are sequentially assigned to non-empty groups whose lengths form the sequence of the natural numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, ...). The length of a group is the number of nodes assigned to it. In other words,
- The
1stnode is assigned to the first group. - The
2ndand the3rdnodes are assigned to the second group. - The
4th,5th, and6thnodes are assigned to the third group, and so on.
Note that the length of the last group may be less than or equal to 1 + the length of the second to last group.
Reverse the nodes in each group with an even length, and return the
head of the modified linked list.
Examples
Example 1
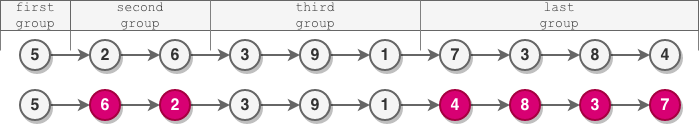
Input: head = [5,2,6,3,9,1,7,3,8,4]
Output: [5,6,2,3,9,1,4,8,3,7]
Explanation:
- The length of the first group is 1, which is odd, hence no reversal occurs.
- The length of the second group is 2, which is even, hence the nodes are reversed.
- The length of the third group is 3, which is odd, hence no reversal occurs.
- The length of the last group is 4, which is even, hence the nodes are reversed.
Example 2
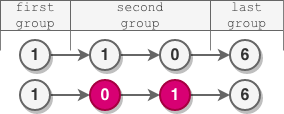
Input: head = [1,1,0,6]
Output: [1,0,1,6]
Explanation:
- The length of the first group is 1. No reversal occurs.
- The length of the second group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
- The length of the last group is 1. No reversal occurs.
Example 3
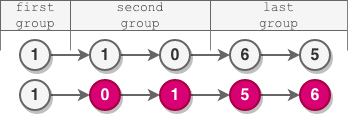
Input: head = [1,1,0,6,5]
Output: [1,0,1,5,6]
Explanation:
- The length of the first group is 1. No reversal occurs.
- The length of the second group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
- The length of the last group is 2. The nodes are reversed.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution
Method 1 - Group Simulation and Reverse
Intuition
We process the linked list in groups of increasing size. For each group, if its length is even, we reverse the group in-place. Otherwise, we leave it as is. This requires careful pointer manipulation.
Approach
Iterate through the list, for each group:
- Count the actual group length (may be less than the intended size at the end).
- If the group length is even, reverse the group and reconnect it.
- Move to the next group, increasing the group size by 1 each time.
Code
C++
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseEvenLengthGroups(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummy(0); dummy.next = head;
ListNode* prev = &dummy;
int group = 1;
while (prev->next) {
ListNode* curr = prev->next;
int cnt = 0;
ListNode* node = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < group && node; ++i, node = node->next) cnt++;
if (cnt % 2 == 0) {
ListNode* tail = curr;
ListNode* next = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) next = next->next;
ListNode* prev2 = next;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {
ListNode* tmp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev2;
prev2 = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
prev->next = prev2;
prev = tail;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) prev = prev->next;
}
group++;
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
Go
type ListNode struct {
Val int
Next *ListNode
}
func reverseEvenLengthGroups(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{Next: head}
prev := dummy
group := 1
for prev.Next != nil {
curr := prev.Next
cnt := 0
node := curr
for i := 0; i < group && node != nil; i++ {
cnt++
node = node.Next
}
if cnt%2 == 0 {
tail := curr
next := curr
for i := 0; i < cnt; i++ { next = next.Next }
prev2 := next
for i := 0; i < cnt; i++ {
tmp := curr.Next
curr.Next = prev2
prev2 = curr
curr = tmp
}
prev.Next = prev2
prev = tail
} else {
for i := 0; i < cnt; i++ { prev = prev.Next }
}
group++
}
return dummy.Next
}
Java
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseEvenLengthGroups(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
int group = 1;
while (prev.next != null) {
ListNode curr = prev.next;
int cnt = 0;
ListNode node = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < group && node != null; i++, node = node.next) cnt++;
if (cnt % 2 == 0) {
ListNode tail = curr;
ListNode next = curr;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) next = next.next;
ListNode prev2 = next;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
ListNode tmp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev2;
prev2 = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
prev.next = prev2;
prev = tail;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) prev = prev.next;
}
group++;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
Kotlin
class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
var next: ListNode? = null
}
class Solution {
fun reverseEvenLengthGroups(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
val dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
var prev: ListNode? = dummy
var group = 1
while (prev?.next != null) {
var curr = prev.next
var cnt = 0
var node = curr
repeat(group) {
if (node != null) {
cnt++
node = node.next
}
}
if (cnt % 2 == 0) {
val tail = curr
var next = curr
repeat(cnt) { next = next?.next }
var prev2 = next
repeat(cnt) {
val tmp = curr?.next
curr?.next = prev2
prev2 = curr
curr = tmp
}
prev.next = prev2
prev = tail
} else {
repeat(cnt) { prev = prev?.next }
}
group++
}
return dummy.next
}
}
Python
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseEvenLengthGroups(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0, head)
prev = dummy
group = 1
while prev.next:
curr = prev.next
cnt = 0
node = curr
for _ in range(group):
if node:
cnt += 1
node = node.next
if cnt % 2 == 0:
tail = curr
next_ = curr
for _ in range(cnt):
next_ = next_.next
prev2 = next_
for _ in range(cnt):
tmp = curr.next
curr.next = prev2
prev2 = curr
curr = tmp
prev.next = prev2
prev = tail
else:
for _ in range(cnt):
prev = prev.next
group += 1
return dummy.next
Rust
// Leetcode's ListNode definition
// pub struct ListNode { pub val: i32, pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>> }
impl Solution {
pub fn reverse_even_length_groups(mut head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode { val: 0, next: head }));
let mut prev = dummy.as_mut();
let mut group = 1;
while let Some(p) = prev {
let mut curr = p.next.as_mut();
let mut cnt = 0;
let mut node = curr.as_ref();
for _ in 0..group {
if let Some(n) = node {
cnt += 1;
node = n.next.as_ref();
}
}
if cnt % 2 == 0 && cnt > 0 {
// Reverse cnt nodes
let mut next = curr.as_mut();
for _ in 0..cnt { if let Some(n) = next { next = n.next.as_mut(); } }
let mut prev2 = next;
for _ in 0..cnt {
if let Some(mut c) = curr.take() {
let tmp = c.next.take();
c.next = prev2.take();
prev2 = Some(c);
curr = tmp;
}
}
p.next = prev2;
for _ in 0..cnt { if let Some(n) = p.next.as_mut() { p = n; } }
prev = Some(p);
} else {
for _ in 0..cnt { if let Some(n) = prev { prev = n.next.as_mut(); } }
}
group += 1;
}
dummy.unwrap().next
}
}
TypeScript
class ListNode {
val: number
next: ListNode | null
constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
}
}
function reverseEvenLengthGroups(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head)
let prev: ListNode | null = dummy
let group = 1
while (prev && prev.next) {
let curr = prev.next
let cnt = 0
let node = curr
for (let i = 0; i < group && node; i++, node = node.next) cnt++
if (cnt % 2 === 0) {
let tail = curr
let next: ListNode | null = curr
for (let i = 0; i < cnt; i++) next = next!.next
let prev2: ListNode | null = next
for (let i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
let tmp = curr!.next
curr!.next = prev2
prev2 = curr
curr = tmp
}
prev.next = prev2
prev = tail
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < cnt; i++) prev = prev!.next
}
group++
}
return dummy.next
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)— each node is visited a constant number of times. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)— in-place reversal, no extra space except pointers.