Search a 2D Matrix 2 - Rows and columns are sorted
Problem
Given a matrix in which each row and each column is sorted, write a method to find an element in it.
OR
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value target in an m x n integer matrix matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
- Integers in each row are sorted in ascending from left to right.
- Integers in each column are sorted in ascending from top to bottom.
Examples
Example 1
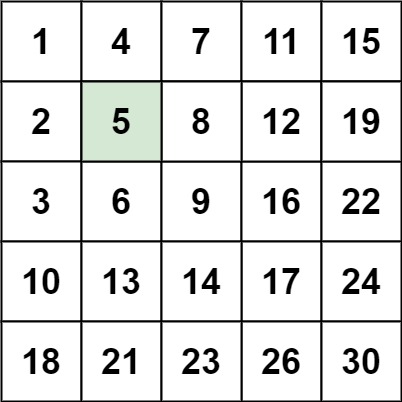
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
Output: true
Example 2
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 20
Output: false
Solution
Here we can have 2 cases -
- Case when array is sorted such that last element of nth row is less than first element of n+1 th row
- Generic case - simply put rows and columns
For case 1, we have already wrote the solution here: [Search a 2D Matrix 1 - Elements sorted row-wise and first integer of each row is greater than last element of previous row](search-a-2d-matrix-1-elements-sorted-row-wise-and-first-integer-of-each-row-is-greater-than-last-element-of-previous-row)
Lets discuss the generic case.
But the matrix could be sorted in a way that the last element of each row is not less than the first element of the next row:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Method 1 – Divide and Conquer (Quad Partition)
Intuition
We can use a divide-and-conquer approach by recursively partitioning the matrix into four quadrants. At each step, we check the center element. If it matches the target, we return true. If the target is less than the center, it cannot be in the bottom-right quadrant (all values there are larger), so we search the other three quadrants. If the target is greater, it cannot be in the top-left quadrant, so we search the other three. This way, we eliminate about a quarter of the matrix at each step.
To visualize, if the center of the matrix is y, the matrix is divided as:
A | B
--+--
C | D
Where:
Ais the upper-left quadrantBis the upper-right quadrantCis the bottom-left quadrantDis the bottom-right quadrant
If the target x is less than y, it cannot be in D (all values there are greater than y), so we search A, B, and C.
If the target x is greater than y, it cannot be in A (all values there are less than y), so we search B, C, and D.
Approach
- Base Case:
- If the submatrix is empty, return false.
- Find Center:
- Compute the middle row and column.
- Compare the center value to the target.
- Recursive Search:
- If equal, return true.
- If target < center, search top-left, top-right, and bottom-left quadrants.
- If target > center, search top-right, bottom-left, and bottom-right quadrants.
Pseudocode
def search(matrix, row_lo, row_hi, col_lo, col_hi, target):
if row_lo > row_hi or col_lo > col_hi:
return False
row_mid = (row_lo + row_hi) // 2
col_mid = (col_lo + col_hi) // 2
mid = matrix[row_mid][col_mid]
if mid == target:
return True
elif target < mid:
return (
search(matrix, row_lo, row_mid - 1, col_lo, col_mid - 1, target) or
search(matrix, row_lo, row_mid - 1, col_mid, col_hi, target) or
search(matrix, row_mid, row_hi, col_lo, col_mid - 1, target)
)
else:
return (
search(matrix, row_lo, row_mid - 1, col_mid + 1, col_hi, target) or
search(matrix, row_mid + 1, row_hi, col_lo, col_mid, target) or
search(matrix, row_mid, row_hi, col_mid + 1, col_hi, target)
)
Code
C++
class Solution {
bool search(const vector<vector<int>>& mat, int r1, int r2, int c1, int c2, int target) {
if (r1 > r2 || c1 > c2) return false;
int rm = (r1 + r2) / 2, cm = (c1 + c2) / 2;
int mid = mat[rm][cm];
if (mid == target) return true;
if (target < mid)
return search(mat, r1, rm - 1, c1, cm - 1, target) ||
search(mat, r1, rm - 1, cm, c2, target) ||
search(mat, rm, r2, c1, cm - 1, target);
else
return search(mat, r1, rm - 1, cm + 1, c2, target) ||
search(mat, rm + 1, r2, c1, cm, target) ||
search(mat, rm, r2, cm + 1, c2, target);
}
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
return search(matrix, 0, m - 1, 0, n - 1, target);
}
};
Go
func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
var search func(r1, r2, c1, c2 int) bool
search = func(r1, r2, c1, c2 int) bool {
if r1 > r2 || c1 > c2 { return false }
rm, cm := (r1+r2)/2, (c1+c2)/2
mid := matrix[rm][cm]
if mid == target { return true }
if target < mid {
return search(r1, rm-1, c1, cm-1) ||
search(r1, rm-1, cm, c2) ||
search(rm, r2, c1, cm-1)
}
return search(r1, rm-1, cm+1, c2) ||
search(rm+1, r2, c1, cm) ||
search(rm, r2, cm+1, c2)
}
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
return search(0, m-1, 0, n-1)
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
return search(matrix, 0, matrix.length - 1, 0, matrix[0].length - 1, target);
}
private boolean search(int[][] mat, int r1, int r2, int c1, int c2, int target) {
if (r1 > r2 || c1 > c2) return false;
int rm = (r1 + r2) / 2, cm = (c1 + c2) / 2;
int mid = mat[rm][cm];
if (mid == target) return true;
if (target < mid)
return search(mat, r1, rm - 1, c1, cm - 1, target) ||
search(mat, r1, rm - 1, cm, c2, target) ||
search(mat, rm, r2, c1, cm - 1, target);
else
return search(mat, r1, rm - 1, cm + 1, c2, target) ||
search(mat, rm + 1, r2, c1, cm, target) ||
search(mat, rm, r2, cm + 1, c2, target);
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun searchMatrix(matrix: Array<IntArray>, target: Int): Boolean {
fun search(r1: Int, r2: Int, c1: Int, c2: Int): Boolean {
if (r1 > r2 || c1 > c2) return false
val rm = (r1 + r2) / 2
val cm = (c1 + c2) / 2
val mid = matrix[rm][cm]
return when {
mid == target -> true
target < mid -> search(r1, rm - 1, c1, cm - 1) ||
search(r1, rm - 1, cm, c2) ||
search(rm, r2, c1, cm - 1)
else -> search(r1, rm - 1, cm + 1, c2) ||
search(rm + 1, r2, c1, cm) ||
search(rm, r2, cm + 1, c2)
}
}
val m = matrix.size
val n = matrix[0].size
return search(0, m - 1, 0, n - 1)
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: list[list[int]], target: int) -> bool:
def search(r1, r2, c1, c2):
if r1 > r2 or c1 > c2:
return False
rm, cm = (r1 + r2) // 2, (c1 + c2) // 2
mid = matrix[rm][cm]
if mid == target:
return True
if target < mid:
return (search(r1, rm - 1, c1, cm - 1) or
search(r1, rm - 1, cm, c2) or
search(rm, r2, c1, cm - 1))
return (search(r1, rm - 1, cm + 1, c2) or
search(rm + 1, r2, c1, cm) or
search(rm, r2, cm + 1, c2))
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
return search(0, m - 1, 0, n - 1)
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
fn search(mat: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, r1: i32, r2: i32, c1: i32, c2: i32, target: i32) -> bool {
if r1 > r2 || c1 > c2 { return false; }
let rm = (r1 + r2) / 2;
let cm = (c1 + c2) / 2;
let mid = mat[rm as usize][cm as usize];
if mid == target { return true; }
if target < mid {
return search(mat, r1, rm - 1, c1, cm - 1, target) ||
search(mat, r1, rm - 1, cm, c2, target) ||
search(mat, rm, r2, c1, cm - 1, target);
}
search(mat, r1, rm - 1, cm + 1, c2, target) ||
search(mat, rm + 1, r2, c1, cm, target) ||
search(mat, rm, r2, cm + 1, c2, target)
}
let m = matrix.len() as i32;
let n = matrix[0].len() as i32;
search(&matrix, 0, m - 1, 0, n - 1, target)
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
searchMatrix(matrix: number[][], target: number): boolean {
function search(r1: number, r2: number, c1: number, c2: number): boolean {
if (r1 > r2 || c1 > c2) return false;
const rm = Math.floor((r1 + r2) / 2);
const cm = Math.floor((c1 + c2) / 2);
const mid = matrix[rm][cm];
if (mid === target) return true;
if (target < mid)
return search(r1, rm - 1, c1, cm - 1) ||
search(r1, rm - 1, cm, c2) ||
search(rm, r2, c1, cm - 1);
return search(r1, rm - 1, cm + 1, c2) ||
search(rm + 1, r2, c1, cm) ||
search(rm, r2, cm + 1, c2);
}
const m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
return search(0, m - 1, 0, n - 1);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^{0.7925}).- Derivation:
- The recurrence is
T(n) = 3T(n/4) + O(1)(since at each step, we search 3 out of 4 quadrants of size n/4). - By the Master Theorem, this solves to
O(n^{log_4 3}). log_4 3 ≈ 0.7925, so the time complexity isO(n^{0.7925}).
- The recurrence is
- Derivation:
- 🧺 Space complexity:
O(\log n), due to recursion stack depth.
Method 2 – Binary Search on Each Row
Intuition
Since each row is sorted, we can perform a binary search on each row to check if the target exists. This leverages the row-wise sorting for efficient searching, but does not use the column-wise sorting.
Approach
- Iterate Over Rows:
- For each row in the matrix, perform a binary search for the target.
- Return Result:
- If the target is found in any row, return true. If not found after all rows, return false.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
for (const auto& row : matrix) {
if (binary_search(row.begin(), row.end(), target)) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
Go
import "sort"
func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
for _, row := range matrix {
i := sort.SearchInts(row, target)
if i < len(row) && row[i] == target {
return true
}
}
return false
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
for (int[] row : matrix) {
int l = 0, r = row.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (row[m] == target) return true;
if (row[m] < target) l = m + 1;
else r = m - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun searchMatrix(matrix: Array<IntArray>, target: Int): Boolean {
for (row in matrix) {
var l = 0
var r = row.size - 1
while (l <= r) {
val m = l + (r - l) / 2
when {
row[m] == target -> return true
row[m] < target -> l = m + 1
else -> r = m - 1
}
}
}
return false
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: list[list[int]], target: int) -> bool:
from bisect import bisect_left
for row in matrix:
i = bisect_left(row, target)
if i < len(row) and row[i] == target:
return True
return False
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
for row in &matrix {
if row.binary_search(&target).is_ok() {
return true;
}
}
false
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
searchMatrix(matrix: number[][], target: number): boolean {
for (const row of matrix) {
let l = 0, r = row.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
const m = Math.floor((l + r) / 2);
if (row[m] === target) return true;
if (row[m] < target) l = m + 1;
else r = m - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m log n), where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns. We perform a binary search on each row. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), since we use only a constant amount of extra space.
Method 3 – Stepwise Linear Search (Top-Right or Bottom-Left)
Intuition
This method leverages the sorted property of both rows and columns. By starting from the top-right (or bottom-left) corner, we can eliminate either a row or a column at each step:
- If the current element is less than the target, move down (since all elements below are larger in the same column).
- If the current element is greater than the target, move left (since all elements to the left are smaller in the same row).
- If the current element matches the target, return true.
This approach efficiently narrows down the search space in a single pass.
Approach
- Start at the top-right corner of the matrix (row = 0, col = n - 1).
- While row and col are within bounds:
- If the current element equals the target, return true.
- If the current element is less than the target, move down (row++).
- If the current element is greater than the target, move left (col--).
- If the loop ends, the target is not present; return false.
Visual Explanation
Suppose we search for 13 in the matrix below:
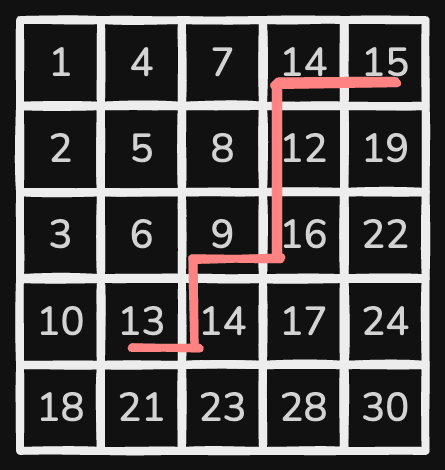
For example, let's search for 13 in Example 1's matrix:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
We start at the top-right element, 15 (row 0, col 4):
- 15 > 13, so move left to 11 (row 0, col 3)
- 11 < 13, so move down to 12 (row 1, col 3)
- 12 < 13, so move down to 16 (row 2, col 3)
- 16 > 13, so move left to 9 (row 2, col 2)
- 9 < 13, so move down to 14 (row 3, col 2)
- 14 > 13, so move left to 13 (row 3, col 1)
- 13 == 13, found!
This stepwise process efficiently narrows down the search space by eliminating either a row or a column at each step.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int row = 0, col = n - 1;
while (row < m && col >= 0) {
if (matrix[row][col] == target) return true;
else if (matrix[row][col] < target) row++;
else col--;
}
return false;
}
};
Go
func searchMatrix(matrix [][]int, target int) bool {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
row, col := 0, n-1
for row < m && col >= 0 {
if matrix[row][col] == target {
return true
} else if matrix[row][col] < target {
row++
} else {
col--
}
}
return false
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int row = 0, col = n - 1;
while (row < m && col >= 0) {
if (matrix[row][col] == target) return true;
else if (matrix[row][col] < target) row++;
else col--;
}
return false;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun searchMatrix(matrix: Array<IntArray>, target: Int): Boolean {
val m = matrix.size
val n = matrix[0].size
var row = 0
var col = n - 1
while (row < m && col >= 0) {
when {
matrix[row][col] == target -> return true
matrix[row][col] < target -> row++
else -> col--
}
}
return false
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: list[list[int]], target: int) -> bool:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
row, col = 0, n - 1
while row < m and col >= 0:
if matrix[row][col] == target:
return True
elif matrix[row][col] < target:
row += 1
else:
col -= 1
return False
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn search_matrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>, target: i32) -> bool {
let (m, n) = (matrix.len(), matrix[0].len());
let (mut row, mut col) = (0, n as i32 - 1);
while row < m && col >= 0 {
let val = matrix[row][col as usize];
if val == target {
return true;
} else if val < target {
row += 1;
} else {
col -= 1;
}
}
false
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
searchMatrix(matrix: number[][], target: number): boolean {
const m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
let row = 0, col = n - 1;
while (row < m && col >= 0) {
if (matrix[row][col] === target) return true;
else if (matrix[row][col] < target) row++;
else col--;
}
return false;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m + n), where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns. In the worst case, we traverse at most m rows and n columns. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), as we use only a constant amount of extra space.