Selling Pieces of Wood
Problem
You are given two integers m and n that represent the height and width of a rectangular piece of wood. You are also given a 2D integer array prices, where prices[i] = [hi, wi, pricei] indicates you can sell a rectangular piece of wood of height hi and width wi for pricei dollars.
To cut a piece of wood, you must make a vertical or horizontal cut across the
entire height or width of the piece to split it into two smaller pieces.
After cutting a piece of wood into some number of smaller pieces, you can sell pieces according to prices. You may sell multiple pieces of the same shape, and you do not have to sell all the shapes. The grain of the wood makes a difference, so you cannot rotate a piece to swap its height and width.
Return _themaximum money you can earn after cutting an _m x n piece of wood.
Note that you can cut the piece of wood as many times as you want.
Examples
Example 1
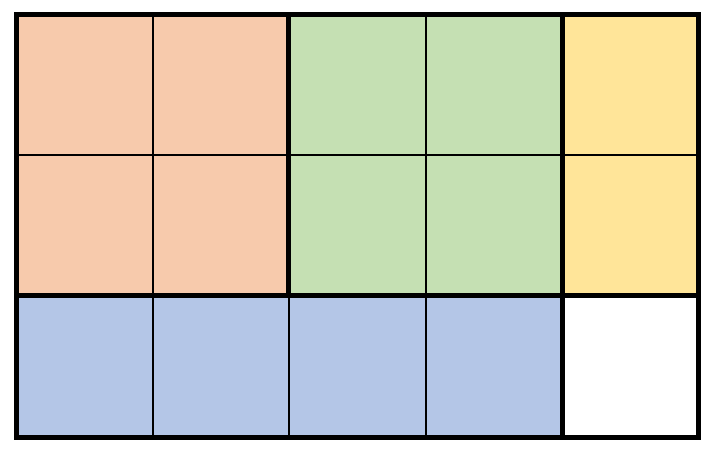
Input: m = 3, n = 5, prices = [[1,4,2],[2,2,7],[2,1,3]]
Output: 19
Explanation: The diagram above shows a possible scenario. It consists of:
- 2 pieces of wood shaped 2 x 2, selling for a price of 2 * 7 = 14.
- 1 piece of wood shaped 2 x 1, selling for a price of 1 * 3 = 3.
- 1 piece of wood shaped 1 x 4, selling for a price of 1 * 2 = 2.
This obtains a total of 14 + 3 + 2 = 19 money earned.
It can be shown that 19 is the maximum amount of money that can be earned.
Example 2
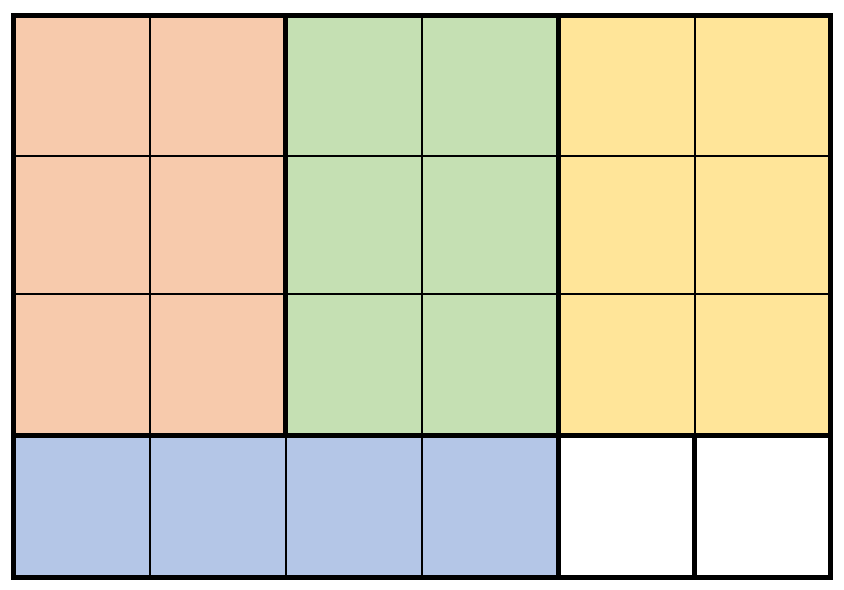
Input: m = 4, n = 6, prices = [[3,2,10],[1,4,2],[4,1,3]]
Output: 32
Explanation: The diagram above shows a possible scenario. It consists of:
- 3 pieces of wood shaped 3 x 2, selling for a price of 3 * 10 = 30.
- 1 piece of wood shaped 1 x 4, selling for a price of 1 * 2 = 2.
This obtains a total of 30 + 2 = 32 money earned.
It can be shown that 32 is the maximum amount of money that can be earned.
Notice that we cannot rotate the 1 x 4 piece of wood to obtain a 4 x 1 piece of wood.
Constraints
1 <= m, n <= 2001 <= prices.length <= 2 * 10^4prices[i].length == 31 <= hi <= m1 <= wi <= n1 <= pricei <= 10^6- All the shapes of wood
(hi, wi)are pairwise distinct.
Solution
Method 1 - DP with Memoization
Intuition
This problem is a classic 2D DP with memoization. For each subrectangle, we want to know the maximum profit we can get by either selling it directly (if a price is given) or by cutting it into smaller pieces and selling those. We recursively try all possible horizontal and vertical cuts, memoizing results to avoid recomputation.
Approach
- Build a price lookup table for all (h, w) pairs.
- Define
dp(h, w)as the maximum profit for a piece of size h x w. - For each (h, w), the answer is the maximum of:
- The direct price (if available)
- The best split by making a horizontal cut at any row (1..h-1)
- The best split by making a vertical cut at any column (1..w-1)
- Use memoization to cache results for each (h, w).
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
long long sellingWood(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& prices) {
vector<vector<long long>> dp(m+1, vector<long long>(n+1, -1));
vector<vector<long long>> price(m+1, vector<long long>(n+1, 0));
for (auto& p : prices) price[p[0]][p[1]] = p[2];
function<long long(int,int)> dfs = [&](int h, int w) -> long long {
if (dp[h][w] != -1) return dp[h][w];
long long res = price[h][w];
for (int i = 1; i < h; ++i)
res = max(res, dfs(i, w) + dfs(h-i, w));
for (int j = 1; j < w; ++j)
res = max(res, dfs(h, j) + dfs(h, w-j));
return dp[h][w] = res;
};
return dfs(m, n);
}
};
Go
func sellingWood(m int, n int, prices [][]int) int64 {
price := make([][]int64, m+1)
for i := range price {
price[i] = make([]int64, n+1)
}
for _, p := range prices {
price[p[0]][p[1]] = int64(p[2])
}
dp := make([][]int64, m+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int64, n+1)
for j := range dp[i] {
dp[i][j] = -1
}
}
var dfs func(int, int) int64
dfs = func(h, w int) int64 {
if dp[h][w] != -1 {
return dp[h][w]
}
res := price[h][w]
for i := 1; i < h; i++ {
res = max64(res, dfs(i, w)+dfs(h-i, w))
}
for j := 1; j < w; j++ {
res = max64(res, dfs(h, j)+dfs(h, w-j))
}
dp[h][w] = res
return res
}
return dfs(m, n)
}
func max64(a, b int64) int64 {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public long sellingWood(int m, int n, int[][] prices) {
long[][] price = new long[m+1][n+1];
for (int[] p : prices) price[p[0]][p[1]] = p[2];
long[][] dp = new long[m+1][n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= m; ++i)
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
return dfs(m, n, price, dp);
}
private long dfs(int h, int w, long[][] price, long[][] dp) {
if (dp[h][w] != -1) return dp[h][w];
long res = price[h][w];
for (int i = 1; i < h; ++i)
res = Math.max(res, dfs(i, w, price, dp) + dfs(h-i, w, price, dp));
for (int j = 1; j < w; ++j)
res = Math.max(res, dfs(h, j, price, dp) + dfs(h, w-j, price, dp));
return dp[h][w] = res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun sellingWood(m: Int, n: Int, prices: Array<IntArray>): Long {
val price = Array(m+1) { LongArray(n+1) }
for (p in prices) price[p[0]][p[1]] = p[2].toLong()
val dp = Array(m+1) { LongArray(n+1) { -1L } }
fun dfs(h: Int, w: Int): Long {
if (dp[h][w] != -1L) return dp[h][w]
var res = price[h][w]
for (i in 1 until h) res = maxOf(res, dfs(i, w) + dfs(h-i, w))
for (j in 1 until w) res = maxOf(res, dfs(h, j) + dfs(h, w-j))
dp[h][w] = res
return res
}
return dfs(m, n)
}
}
Python
from functools import lru_cache
def sellingWood(m, n, prices):
price = [[0]*(n+1) for _ in range(m+1)]
for h, w, p in prices:
price[h][w] = p
@lru_cache(None)
def dp(h, w):
res = price[h][w]
for i in range(1, h):
res = max(res, dp(i, w) + dp(h-i, w))
for j in range(1, w):
res = max(res, dp(h, j) + dp(h, w-j))
return res
return dp(m, n)
Rust
use std::collections::HashMap;
pub fn selling_wood(m: i32, n: i32, prices: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i64 {
let m = m as usize;
let n = n as usize;
let mut price = vec![vec![0i64; n+1]; m+1];
for p in prices.iter() {
price[p[0] as usize][p[1] as usize] = p[2] as i64;
}
let mut memo = vec![vec![-1i64; n+1]; m+1];
fn dp(h: usize, w: usize, price: &Vec<Vec<i64>>, memo: &mut Vec<Vec<i64>>) -> i64 {
if memo[h][w] != -1 { return memo[h][w]; }
let mut res = price[h][w];
for i in 1..h {
res = res.max(dp(i, w, price, memo) + dp(h-i, w, price, memo));
}
for j in 1..w {
res = res.max(dp(h, j, price, memo) + dp(h, w-j, price, memo));
}
memo[h][w] = res;
res
}
dp(m, n, &price, &mut memo)
}
TypeScript
function sellingWood(m: number, n: number, prices: number[][]): number {
const price: number[][] = Array.from({length: m+1}, () => Array(n+1).fill(0));
for (const [h, w, p] of prices) price[h][w] = p;
const dp: number[][] = Array.from({length: m+1}, () => Array(n+1).fill(-1));
function dfs(h: number, w: number): number {
if (dp[h][w] !== -1) return dp[h][w];
let res = price[h][w];
for (let i = 1; i < h; ++i) res = Math.max(res, dfs(i, w) + dfs(h-i, w));
for (let j = 1; j < w; ++j) res = Math.max(res, dfs(h, j) + dfs(h, w-j));
dp[h][w] = res;
return res;
}
return dfs(m, n);
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n * (m + n))(since for each (h, w), we try all possible cuts) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n)(for memoization)