Shortest Distance from All Buildings
Problem
You are given an m x n grid grid of values 0, 1, or 2, where:
- each
0marks an empty land that you can pass by freely, - each
1marks a building that you cannot pass through, and - each
2marks an obstacle that you cannot pass through.
You want to build a house on an empty land that reaches all buildings in the shortest total travel distance. You can only move up, down, left, and right.
Return the shortest travel distance for such a house. If it is not possible to build such a house according to the above rules, return -1.
The total travel distance is the sum of the distances between the houses of the friends and the meeting point.
The distance is calculated using Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
Examples
Example 1
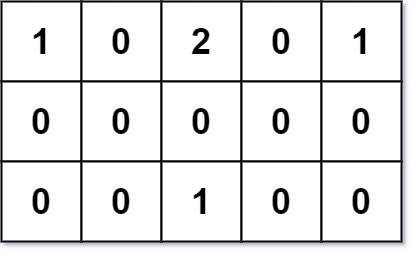
Input: grid = [[1,0,2,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]]
Output: 7
Explanation: Given three buildings at (0,0), (0,4), (2,2), and an obstacle at (0,2).
The point (1,2) is an ideal empty land to build a house, as the total travel distance of 3+3+1=7 is minimal.
So return 7.
Example 2
Input: grid = [[1,0]]
Output: 1
Example 3
Input: grid = [[1]]
Output: -1
Constraints
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 50grid[i][j]is either0,1, or2.- There will be at least one building in the
grid.
Solution
Method 1 - BFS from Each Building
Intuition
For each building, we perform BFS to calculate the shortest distance from that building to every empty land. We accumulate the total distance and track how many buildings can reach each cell. The answer is the minimum total distance among all empty lands that can be reached by all buildings.
Approach
- For each building, run BFS to update two matrices:
distance[i][j]: total distance from all buildings to cell(i, j).numReach[i][j]: number of buildings that can reach cell(i, j).
- After BFS from all buildings, for each empty land cell, if it can be reached by all buildings, update the answer with its total distance.
- If no such cell exists, return -1.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> distance(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
vector<vector<int>> reach(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
int numBuildings = 0;
vector<pair<int, int>> dirs = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
numBuildings++;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({i, j});
int dist = 0;
visited[i][j] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
dist++;
for (int k = 0; k < sz; ++k) {
auto [x, y] = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto& d : dirs) {
int nx = x + d.first, ny = y + d.second;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 0) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
distance[nx][ny] += dist;
reach[nx][ny]++;
q.push({nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
int res = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0 && reach[i][j] == numBuildings) {
res = min(res, distance[i][j]);
}
}
}
return res == INT_MAX ? -1 : res;
}
};
Go
func shortestDistance(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
distance := make([][]int, m)
reach := make([][]int, m)
for i := range distance {
distance[i] = make([]int, n)
reach[i] = make([]int, n)
}
dirs := [][]int{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}
numBuildings := 0
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
numBuildings++
visited := make([][]bool, m)
for k := range visited {
visited[k] = make([]bool, n)
}
q := [][2]int{{i, j}}
dist := 0
visited[i][j] = true
for len(q) > 0 {
dist++
sz := len(q)
for k := 0; k < sz; k++ {
x, y := q[0][0], q[0][1]
q = q[1:]
for _, d := range dirs {
nx, ny := x+d[0], y+d[1]
if nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 0 {
visited[nx][ny] = true
distance[nx][ny] += dist
reach[nx][ny]++
q = append(q, [2]int{nx, ny})
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
res := 1<<31 - 1
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 0 && reach[i][j] == numBuildings {
if distance[i][j] < res {
res = distance[i][j]
}
}
}
}
if res == 1<<31-1 {
return -1
}
return res
}
Java
class Solution {
public int shortestDistance(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] distance = new int[m][n];
int[][] reach = new int[m][n];
int numBuildings = 0;
int[][] dirs = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
numBuildings++;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
int dist = 0;
visited[i][j] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
dist++;
int sz = q.size();
for (int k = 0; k < sz; k++) {
int[] curr = q.poll();
for (int[] d : dirs) {
int nx = curr[0] + d[0], ny = curr[1] + d[1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 0) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
distance[nx][ny] += dist;
reach[nx][ny]++;
q.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0 && reach[i][j] == numBuildings) {
res = Math.min(res, distance[i][j]);
}
}
}
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun shortestDistance(grid: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val distance = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
val reach = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
val dirs = arrayOf(intArrayOf(0,1), intArrayOf(1,0), intArrayOf(0,-1), intArrayOf(-1,0))
var numBuildings = 0
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
numBuildings++
val visited = Array(m) { BooleanArray(n) }
val q: Queue<Pair<Int, Int>> = LinkedList()
q.offer(Pair(i, j))
var dist = 0
visited[i][j] = true
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
dist++
repeat(q.size) {
val (x, y) = q.poll()
for (d in dirs) {
val nx = x + d[0]
val ny = y + d[1]
if (nx in 0 until m && ny in 0 until n && !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 0) {
visited[nx][ny] = true
distance[nx][ny] += dist
reach[nx][ny]++
q.offer(Pair(nx, ny))
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
var res = Int.MAX_VALUE
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0 && reach[i][j] == numBuildings) {
res = minOf(res, distance[i][j])
}
}
}
return if (res == Int.MAX_VALUE) -1 else res
}
}
Python
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def shortestDistance(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
distance = [[0]*n for _ in range(m)]
reach = [[0]*n for _ in range(m)]
dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)]
numBuildings = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
numBuildings += 1
visited = [[False]*n for _ in range(m)]
q = deque([(i, j)])
dist = 0
visited[i][j] = True
while q:
dist += 1
for _ in range(len(q)):
x, y = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x+dx, y+dy
if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and not visited[nx][ny] and grid[nx][ny] == 0:
visited[nx][ny] = True
distance[nx][ny] += dist
reach[nx][ny] += 1
q.append((nx, ny))
res = float('inf')
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == 0 and reach[i][j] == numBuildings:
res = min(res, distance[i][j])
return -1 if res == float('inf') else res
Rust
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn shortest_distance(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut distance = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
let mut reach = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
let dirs = [(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1),(-1,0)];
let mut num_buildings = 0;
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
num_buildings += 1;
let mut visited = vec![vec![false; n]; m];
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back((i, j));
let mut dist = 0;
visited[i][j] = true;
while !q.is_empty() {
dist += 1;
for _ in 0..q.len() {
let (x, y) = q.pop_front().unwrap();
for (dx, dy) in dirs.iter() {
let nx = x as i32 + dx;
let ny = y as i32 + dy;
if nx >= 0 && nx < m as i32 && ny >= 0 && ny < n as i32 {
let nx = nx as usize;
let ny = ny as usize;
if !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 0 {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
distance[nx][ny] += dist;
reach[nx][ny] += 1;
q.push_back((nx, ny));
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
let mut res = std::i32::MAX;
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if grid[i][j] == 0 && reach[i][j] == num_buildings {
res = res.min(distance[i][j]);
}
}
}
if res == std::i32::MAX { -1 } else { res }
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
shortestDistance(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const distance = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(0));
const reach = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(0));
const dirs = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,-1],[-1,0]];
let numBuildings = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
numBuildings++;
const visited = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(false));
const q: [number, number][] = [[i, j]];
let dist = 0;
visited[i][j] = true;
while (q.length) {
dist++;
const sz = q.length;
for (let k = 0; k < sz; k++) {
const [x, y] = q.shift()!;
for (const [dx, dy] of dirs) {
const nx = x + dx, ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] === 0) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
distance[nx][ny] += dist;
reach[nx][ny]++;
q.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
let res = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] === 0 && reach[i][j] === numBuildings) {
res = Math.min(res, distance[i][j]);
}
}
}
return res === Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ? -1 : res;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m*n*B), whereBis the number of buildings (each BFS visits all cells). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m*n)for the distance and reach matrices.