Shortest Path in a Weighted Tree
Problem
You are given an integer n and an undirected, weighted tree rooted at node 1 with n nodes numbered from 1 to n. This is represented by a 2D array
edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates an undirected edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length q, where each
queries[i] is either:
[1, u, v, w']- Update the weight of the edge between nodesuandvtow', where(u, v)is guaranteed to be an edge present inedges.[2, x]- Compute the shortest path distance from the root node 1 to nodex.
Return an integer array answer, where answer[i] is the shortest path distance from node 1 to x for the ith query of [2, x].
Examples
Example 1
Input: n = 2, edges = [[1,2,7]], queries = [[2,2],[1,1,2,4],[2,2]]
Output: [7,4]
Explanation:
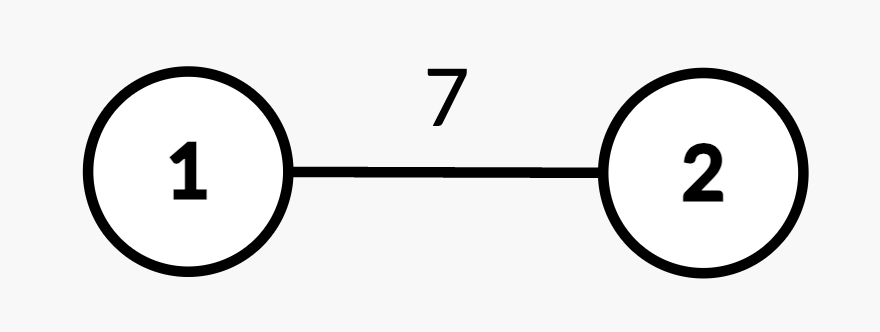
* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 7.
* Query `[1,1,2,4]`: The weight of edge `(1,2)` changes from 7 to 4.
* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 4.
Example 2
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,2,2],[1,3,4]], queries =
[[2,1],[2,3],[1,1,3,7],[2,2],[2,3]]
Output: [0,4,2,7]
Explanation:
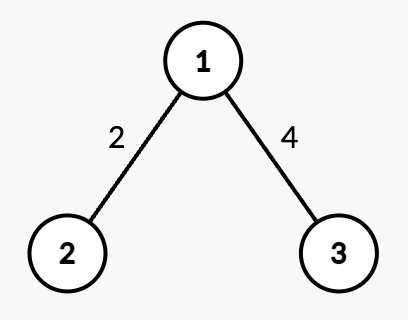
* Query `[2,1]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 1 is 0.
* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 is 4.
* Query `[1,1,3,7]`: The weight of edge `(1,3)` changes from 4 to 7.
* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 2.
* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 is 7.
Example 3
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,5]], queries =
[[2,4],[2,3],[1,2,3,3],[2,2],[2,3]]
Output: [8,3,2,5]
Explanation:
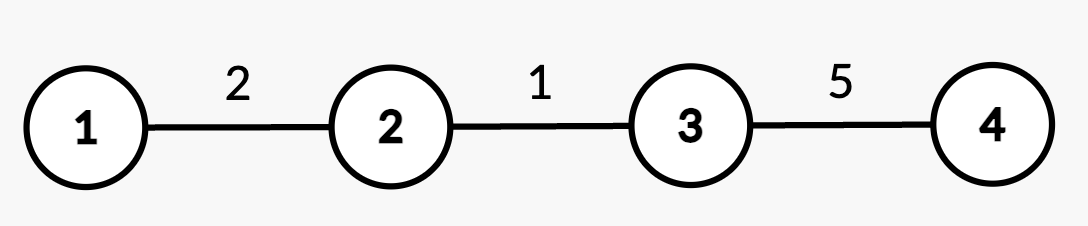
* Query `[2,4]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 4 consists of edges `(1,2)`, `(2,3)`, and `(3,4)` with weights `2 + 1 + 5 = 8`.
* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 consists of edges `(1,2)` and `(2,3)` with weights `2 + 1 = 3`.
* Query `[1,2,3,3]`: The weight of edge `(2,3)` changes from 1 to 3.
* Query `[2,2]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 2 is 2.
* Query `[2,3]`: The shortest path from root node 1 to node 3 consists of edges `(1,2)` and `(2,3)` with updated weights `2 + 3 = 5`.
Constraints
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i] == [ui, vi, wi]1 <= ui, vi <= n1 <= wi <= 10^4- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree. 1 <= queries.length == q <= 10^5queries[i].length == 2or4queries[i] == [1, u, v, w']or,queries[i] == [2, x]1 <= u, v, x <= n(u, v)is always an edge fromedges.1 <= w' <= 10^4
Solution
Method 1 – Euler Tour + Binary Indexed Tree (Fenwick Tree)
Intuition
We need to support two operations efficiently:
- Update the weight of an edge.
- Query the shortest path from the root to any node.
Since the tree is rooted at 1, the shortest path from 1 to x is the sum of edge weights along the path. We can flatten the tree using an Euler tour, and use a Binary Indexed Tree (BIT) or Segment Tree to support fast range updates and point queries.
Approach
- Build the tree and assign each node an entry time (in-time) via DFS.
- For each edge, store its index and which child it connects to.
- Use a BIT to maintain the prefix sum of weights from the root to each node.
- For an update, update the BIT for the subtree of the child node.
- For a query, query the BIT at the in-time of the node.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class BIT {
vector<long long> t; int n;
public:
BIT(int sz): t(sz+2), n(sz+2) {}
void add(int i, long long v) { for (; i < n; i += i&-i) t[i] += v; }
long long sum(int i) { long long r=0; for (; i; i -= i&-i) r += t[i]; return r; }
void range(int l, int r, long long v) { add(l, v); add(r+1, -v); }
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> shortestPath(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(n+1);
map<pair<int,int>, int> edgeIdx;
vector<int> eid(n+1), parent(n+1), in(n+1), out(n+1), weight(n);
for (int i=0; i<edges.size(); ++i) {
int u=edges[i][0], v=edges[i][1], w=edges[i][2];
g[u].push_back({v,w}); g[v].push_back({u,w});
edgeIdx[{u,v}] = edgeIdx[{v,u}] = i;
weight[i] = w;
}
int time=1;
function<void(int,int)> dfs = [&](int u, int p) {
in[u]=time++;
for (auto& [v,w]:g[u]) if (v!=p) {
parent[v]=u;
eid[v]=edgeIdx[{u,v}];
dfs(v,u);
}
out[u]=time-1;
};
dfs(1,0);
BIT bit(n+2);
for (int v=2; v<=n; ++v) bit.range(in[v], in[v], weight[eid[v]]);
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& q:queries) {
if (q[0]==1) {
int u=q[1], v=q[2], w=q[3];
int ch = parent[u]==v?u:v;
int idx = eid[ch];
int diff = w-weight[idx];
bit.range(in[ch], out[ch], diff);
weight[idx]=w;
} else {
int x=q[1];
ans.push_back(bit.sum(in[x]));
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static class BIT {
long[] t;
int n;
BIT(int sz) { t = new long[sz+2]; n = sz+2; }
void add(int i, long v) { for (; i < n; i += i&-i) t[i] += v; }
long sum(int i) { long r=0; for (; i>0; i -= i&-i) r += t[i]; return r; }
void range(int l, int r, long v) { add(l, v); add(r+1, -v); }
}
public List<Integer> shortestPath(int n, int[][] edges, int[][] queries) {
List<int[]>[] g = new List[n+1];
for (int i=0; i<=n; ++i) g[i]=new ArrayList<>();
Map<String,Integer> edgeIdx = new HashMap<>();
int[] eid = new int[n+1], parent = new int[n+1], in = new int[n+1], out = new int[n+1], weight = new int[n];
for (int i=0; i<edges.length; ++i) {
int u=edges[i][0], v=edges[i][1], w=edges[i][2];
g[u].add(new int[]{v,w}); g[v].add(new int[]{u,w});
edgeIdx.put(u+","+v, i); edgeIdx.put(v+","+u, i);
weight[i]=w;
}
int[] time = {1};
dfs(1,0,g,parent,eid,edgeIdx,in,out,time);
BIT bit = new BIT(n+2);
for (int v=2; v<=n; ++v) bit.range(in[v], in[v], weight[eid[v]]);
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] q:queries) {
if (q[0]==1) {
int u=q[1], v=q[2], w=q[3];
int ch = parent[u]==v?u:v;
int idx = eid[ch];
int diff = w-weight[idx];
bit.range(in[ch], out[ch], diff);
weight[idx]=w;
} else {
int x=q[1];
ans.add((int)bit.sum(in[x]));
}
}
return ans;
}
static void dfs(int u, int p, List<int[]>[] g, int[] parent, int[] eid, Map<String,Integer> edgeIdx, int[] in, int[] out, int[] time) {
in[u]=time[0]++;
for (int[] vw:g[u]) if (vw[0]!=p) {
parent[vw[0]]=u;
eid[vw[0]]=edgeIdx.get(u+","+vw[0]);
dfs(vw[0],u,g,parent,eid,edgeIdx,in,out,time);
}
out[u]=time[0]-1;
}
}
Python
class BIT:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n+2
self.t = [0]*(self.n)
def add(self, i, v):
while i < self.n:
self.t[i] += v
i += i&-i
def sum(self, i):
r = 0
while i:
r += self.t[i]
i -= i&-i
return r
def range(self, l, r, v):
self.add(l, v)
self.add(r+1, -v)
class Solution:
def shortestPath(self, n, edges, queries):
from collections import defaultdict
g = defaultdict(list)
edgeIdx = dict()
weight = [0]*n
for i, (u,v,w) in enumerate(edges):
g[u].append((v,w))
g[v].append((u,w))
edgeIdx[(u,v)] = edgeIdx[(v,u)] = i
weight[i] = w
in_time = [0]*(n+1)
out_time = [0]*(n+1)
parent = [0]*(n+1)
eid = [0]*(n+1)
time = [1]
def dfs(u, p):
in_time[u]=time[0]
time[0]+=1
for v,w in g[u]:
if v!=p:
parent[v]=u
eid[v]=edgeIdx[(u,v)]
dfs(v,u)
out_time[u]=time[0]-1
dfs(1,0)
bit = BIT(n+2)
for v in range(2,n+1):
bit.range(in_time[v], in_time[v], weight[eid[v]])
ans = []
for q in queries:
if q[0]==1:
u,v,w = q[1:]
ch = u if parent[u]==v else v
idx = eid[ch]
diff = w-weight[idx]
bit.range(in_time[ch], out_time[ch], diff)
weight[idx]=w
else:
x = q[1]
ans.append(bit.sum(in_time[x]))
return ans
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O((n+q) log n)— Each update/query is O(log n), preprocessing is O(n). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)— For the tree, BIT, and auxiliary arrays.