Smallest String With Swaps
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a string s, and an array of pairs of indices in the string pairs where pairs[i] = [a, b] indicates 2 indices(0-indexed) of the string.
You can swap the characters at any pair of indices in the given pairs any number of times.
Return the lexicographically smallest string that s can be changed to after using the swaps.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: s = "dcab", pairs = [[0,3],[1,2]]
Output: "bacd"
Explaination:
Swap s[0] and s[3], s = "bcad"
Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "bacd"
Example 2:
Input: s = "dcab", pairs = [[0,3],[1,2],[0,2]]
Output: "abcd"
Explaination:
Swap s[0] and s[3], s = "bcad"
Swap s[0] and s[2], s = "acbd"
Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "abcd"
Example 3:
Input: s = "cba", pairs = [[0,1],[1,2]]
Output: "abc"
Explaination:
Swap s[0] and s[1], s = "bca"
Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "bac"
Swap s[0] and s[1], s = "abc"
Solution
Method 1 – Union Find (Disjoint Set)
Intuition
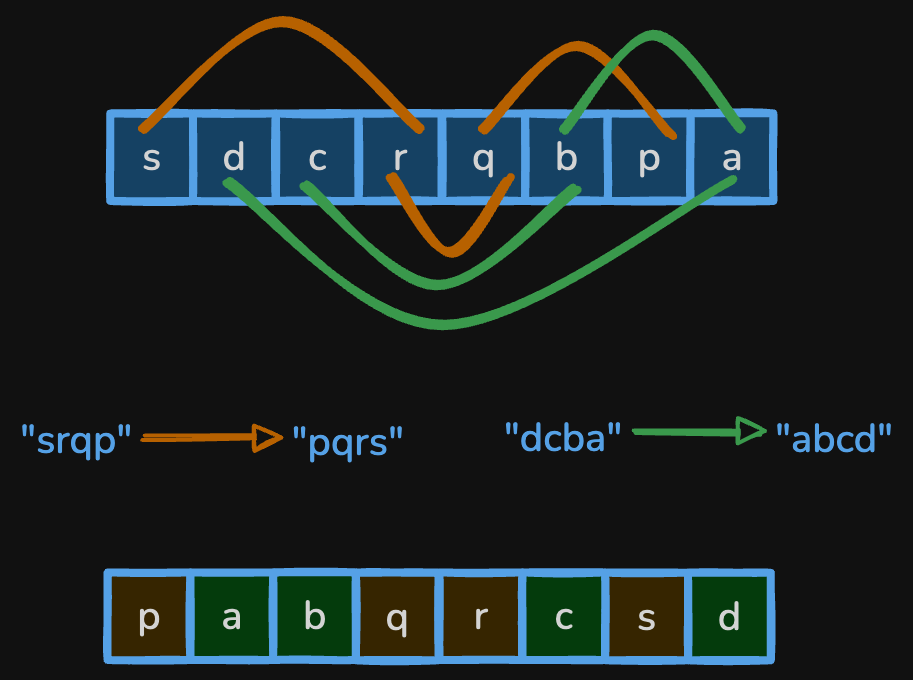
If a set of indices are connected by swap pairs, the characters at those indices can be freely rearranged among themselves. For example, in the string:
"sdcrqbpa"
[[0,3],[4,6],[3,4],[1,7],[2,5],[5,7]]
there are two groups of interconnected indices, so we can rearrange the characters within each group to achieve the lexicographically smallest string.
Approach
- Use union-find to group indices that can be swapped with each other.
- For each group, collect the characters and sort them (using a min-heap or priority queue).
- Reconstruct the result by picking the smallest available character for each index from its group.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string smallestStringWithSwaps(string s, vector<vector<int>>& pairs) {
int n = s.size();
vector<int> p(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) p[i] = i;
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) { return p[x] == x ? x : p[x] = find(p[x]); };
for (auto& e : pairs) {
int a = find(e[0]), b = find(e[1]);
if (a != b) p[b] = a;
}
unordered_map<int, priority_queue<char, vector<char>, greater<char>>> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) mp[find(i)].push(s[i]);
string res;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) res += mp[find(i)].top(), mp[find(i)].pop();
return res;
}
};
Go
import "container/heap"
type PQ []byte
func (pq PQ) Len() int { return len(pq) }
func (pq PQ) Less(i, j int) bool { return pq[i] < pq[j] }
func (pq PQ) Swap(i, j int) { pq[i], pq[j] = pq[j], pq[i] }
func (pq *PQ) Push(x interface{}) { *pq = append(*pq, x.(byte)) }
func (pq *PQ) Pop() interface{} { old := *pq; x := old[len(old)-1]; *pq = old[:len(old)-1]; return x }
func smallestStringWithSwaps(s string, pairs [][]int) string {
n := len(s)
p := make([]int, n)
for i := range p { p[i] = i }
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int { if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p[x]) }; return p[x] }
for _, e := range pairs {
a, b := find(e[0]), find(e[1])
if a != b { p[b] = a }
}
mp := map[int]*PQ{}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
root := find(i)
if mp[root] == nil { mp[root] = &PQ{} }
heap.Push(mp[root], s[i])
}
res := make([]byte, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
root := find(i)
res[i] = heap.Pop(mp[root]).(byte)
}
return string(res)
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String smallestStringWithSwaps(String s, List<List<Integer>> pairs) {
int n = s.length();
int[] p = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) p[i] = i;
for (List<Integer> edge : pairs) {
int a = find(p, edge.get(0)), b = find(p, edge.get(1));
if (a != b) p[b] = a;
}
Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Character>> mp = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int root = find(p, i);
mp.computeIfAbsent(root, k -> new PriorityQueue<>());
mp.get(root).add(s.charAt(i));
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int root = find(p, i);
sb.append(mp.get(root).poll());
}
return sb.toString();
}
private int find(int[] p, int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p, p[x]);
return p[x];
}
}
Kotlin
import java.util.*
class Solution {
fun smallestStringWithSwaps(s: String, pairs: List<List<Int>>): String {
val n = s.length
val p = IntArray(n) { it }
fun find(x: Int): Int { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x] }
for (e in pairs) {
val a = find(e[0]); val b = find(e[1])
if (a != b) p[b] = a
}
val mp = mutableMapOf<Int, PriorityQueue<Char>>()
for (i in 0 until n) {
val root = find(i)
mp.computeIfAbsent(root) { PriorityQueue() }.add(s[i])
}
val sb = StringBuilder()
for (i in 0 until n) {
val root = find(i)
sb.append(mp[root]!!.poll())
}
return sb.toString()
}
}
Python
import heapq
class Solution:
def smallestStringWithSwaps(self, s: str, pairs: list[list[int]]) -> str:
n = len(s)
p = list(range(n))
def find(x):
if p[x] != x: p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
for a, b in pairs:
pa, pb = find(a), find(b)
if pa != pb: p[pb] = pa
mp = {}
for i, ch in enumerate(s):
root = find(i)
if root not in mp: mp[root] = []
heapq.heappush(mp[root], ch)
res = []
for i in range(n):
root = find(i)
res.append(heapq.heappop(mp[root]))
return ''.join(res)
Rust
use std::collections::{HashMap, BinaryHeap};
use std::cmp::Reverse;
impl Solution {
pub fn smallest_string_with_swaps(s: String, pairs: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> String {
let n = s.len();
let mut p: Vec<usize> = (0..n).collect();
fn find(p: &mut Vec<usize>, x: usize) -> usize {
if p[x] != x { p[x] = find(p, p[x]); } p[x]
}
for e in &pairs {
let a = find(&mut p, e[0] as usize);
let b = find(&mut p, e[1] as usize);
if a != b { p[b] = a; }
}
let mut mp: HashMap<usize, BinaryHeap<Reverse<u8>>> = HashMap::new();
let s_bytes = s.as_bytes();
for i in 0..n {
let root = find(&mut p, i);
mp.entry(root).or_default().push(Reverse(s_bytes[i]));
}
let mut res = vec![0u8; n];
for i in 0..n {
let root = find(&mut p, i);
res[i] = mp.get_mut(&root).unwrap().pop().unwrap().0;
}
String::from_utf8(res).unwrap()
}
}
TypeScript
function smallestStringWithSwaps(s: string, pairs: number[][]): string {
const n = s.length;
const p = Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => i);
function find(x: number): number {
if (p[x] !== x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
for (const [a, b] of pairs) {
const pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa !== pb) p[pb] = pa;
}
const mp: Record<number, string[]> = {};
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const root = find(i);
if (!mp[root]) mp[root] = [];
mp[root].push(s[i]);
}
for (const arr of Object.values(mp)) arr.sort();
const idx: Record<number, number> = {};
let res = '';
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const root = find(i);
idx[root] = (idx[root] || 0);
res += mp[root][idx[root]++];
}
return res;
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(N log N + M)whereNis the string length andMis the number of pairs (for union-find and sorting each group). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(N + M)for the union-find structure and groupings.