Snail Traversal
Problem
Write code that enhances all arrays such that you can call the
snail(rowsCount, colsCount) method that transforms the 1D array into a 2D array organised in the pattern known as snail traversal order. Invalid input values should output an empty array. If rowsCount * colsCount !== nums.length, the input is considered invalid.
Snail traversal order _ _ starts at the top left cell with the first value of the current array. It then moves through the entire first column from top to bottom, followed by moving to the next column on the right and traversing it from bottom to top. This pattern continues, alternating the direction of traversal with each column, until the entire current array is covered. For example, when given the input array [19, 10, 3, 7, 9, 8, 5, 2, 1, 17, 16, 14, 12, 18, 6, 13, 11, 20, 4, 15] with rowsCount = 5 and colsCount = 4, the desired output matrix is shown below. Note that iterating the matrix following the arrows corresponds to the order of numbers in the original array.
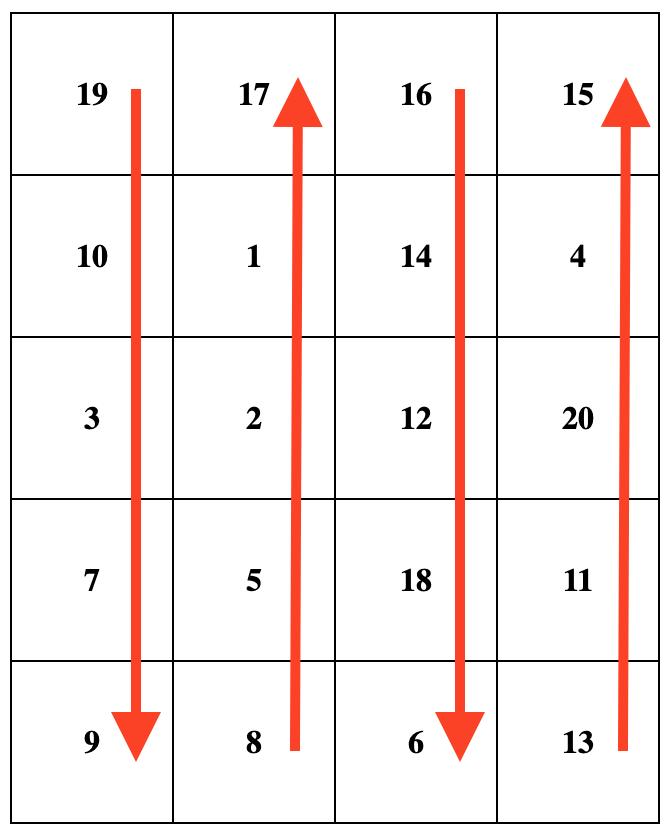
Examples
Example 1
Input:
nums = [19, 10, 3, 7, 9, 8, 5, 2, 1, 17, 16, 14, 12, 18, 6, 13, 11, 20, 4, 15]
rowsCount = 5
colsCount = 4
Output:
[
[19,17,16,15],
[10,1,14,4],
[3,2,12,20],
[7,5,18,11],
[9,8,6,13]
]
Example 2
Input:
nums = [1,2,3,4]
rowsCount = 1
colsCount = 4
Output: [[1, 2, 3, 4]]
Example 3
Input:
nums = [1,3]
rowsCount = 2
colsCount = 2
Output: []
Explanation: 2 multiplied by 2 is 4, and the original array [1,3] has a length of 2; therefore, the input is invalid.
Constraints
0 <= nums.length <= 2501 <= nums[i] <= 10001 <= rowsCount <= 2501 <= colsCount <= 250
Solution
Method 1 – Simulate Snail Traversal by Column
Intuition
The snail traversal fills the matrix column by column, alternating direction for each column. We can simulate this by iterating through the columns and, for each, filling the rows from top-to-bottom or bottom-to-top depending on the column's parity.
Approach
- Check if
rowsCount * colsCount !== nums.length. If so, return an empty array. - Initialize a 2D array of size
rowsCount x colsCount. - For each column:
- If the column index is even, fill from top to bottom.
- If odd, fill from bottom to top.
- Fill the matrix with the elements from the original array in order.
- Return the filled matrix.
Code
JavaScript
Array.prototype.snail = function(rowsCount, colsCount) {
if (rowsCount * colsCount !== this.length) return [];
const ans = Array.from({length: rowsCount}, () => Array(colsCount));
let k = 0;
for (let c = 0; c < colsCount; ++c) {
if (c % 2 === 0) {
for (let r = 0; r < rowsCount; ++r) ans[r][c] = this[k++];
} else {
for (let r = rowsCount - 1; r >= 0; --r) ans[r][c] = this[k++];
}
}
return ans;
}
TypeScript
declare global {
interface Array<T> {
snail(rowsCount: number, colsCount: number): T[][];
}
}
Array.prototype.snail = function<T>(rowsCount: number, colsCount: number): T[][] {
if (rowsCount * colsCount !== this.length) return [];
const ans: T[][] = Array.from({length: rowsCount}, () => Array(colsCount));
let k = 0;
for (let c = 0; c < colsCount; ++c) {
if (c % 2 === 0) {
for (let r = 0; r < rowsCount; ++r) ans[r][c] = this[k++];
} else {
for (let r = rowsCount - 1; r >= 0; --r) ans[r][c] = this[k++];
}
}
return ans;
}
export {};
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the length of the input array. Each element is placed exactly once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the output 2D array of the same size as the input.