Subsets 1
Problem
Given a set of distinct integers/characters, S, return all possible subsets.
OR
Given an integer array
numsof unique elements, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Examples
If we're given a set of integers such that S = {1, 2, 3}, how can we find all the subsets of that set? For example, given S, the set of all subsets i.e. P(S) we get are {}, {1}, {2}, {3}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, and {1, 2, 3}. Here is {} is empty set denoted by Φ.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0]
Output:[[],[0]]
Follow up - [Subsets II](subsets-2)
Definition
[Subarrays vs Subsequences vs Subsets Definition](subarrays-vs-subsequences-vs-subsets-definition)
Solution
If S has n elements in it then P(s) will have 2^n elements. P(S) is also called power set.
Method 1 - Use Backtracking
This can be solved in couple of ways using recursion, backtracking. This is similar to [Print All Combinations of subset of size K from Given Array](print-all-combinations-of-subset-of-size-k-from-given-array).
At each index in input array, we have to choose whether we have to choose a number or not.
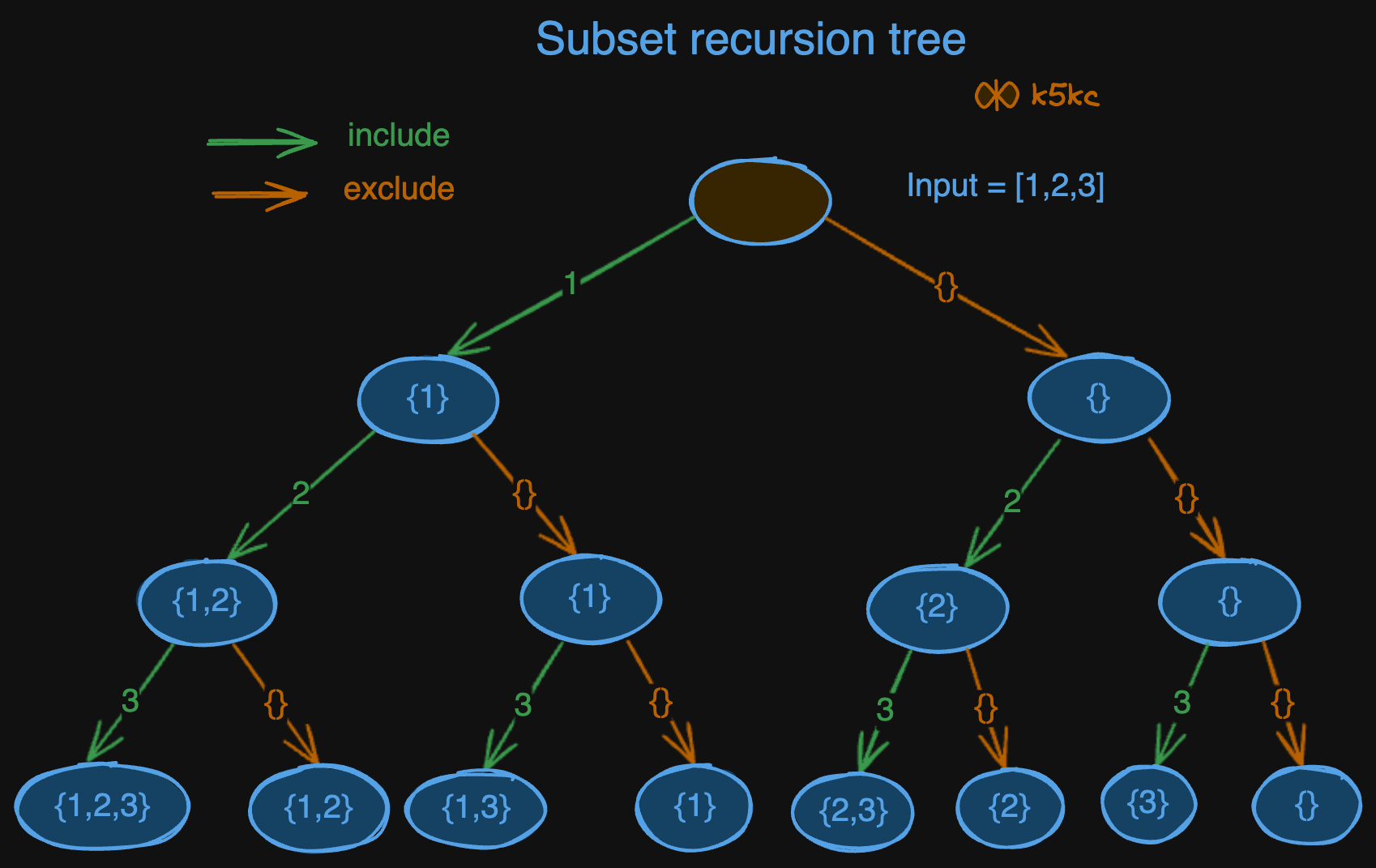
Video Explanation
Here is the video explanation: <div class="youtube-embed"><iframe src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/6MdalEAjuB0" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></div>
Thought Process 1 - Focus One Element at Each Level
Each recursion level focuses on one element, we need to decide choose or not choose this element. (Every level split into 2 branches.)
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(nums, 0, ans, new ArrayList<>());
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int idx, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> subAns) {
if (idx >= nums.length){
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(subAns));
return;
}
// include the number in the set
subAns.add(nums[idx]);
dfs(nums, idx+1, ans, subAns);
// don't include the number in the set
subAns.remove(subAns.size() - 1);
dfs(nums, idx+1, ans, subAns);
}
Thought Process 2 - Focus on All the Following Elements at Each Level
Each recursion level focuses on all the following elements. We scan through all the following elements and decide whether to choose or not choose that element. (Every level split into N branches.)
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(ans, new ArrayList<>(), nums, 0);
return ans;
}
private void backtrack(int [] nums, int idx, List<List<Integer>> ans , List<Integer> subAns){
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(subAns));
for(int i = idx; i < nums.length; i++){
subAns.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, i + 1, ans, subAns);
subAns.remove(subAns.size() - 1);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n.2^n)(as we are taking call between 2 (yes or no) paths for n elements)
Method 2 - Using Bit Manipulation and Iterative
We know total number of sets is 2^n. We can loop through each solution from 0 to 2^n - 1. For each case, we add a value or not.
Example
Consider the set:
A = {a, b, c}
So, we need 3 bits, and 2^3 answers:
Pseudocode
subsets(A, N):
for i = 0 to 2^N:
for j = 0 to N:
if jth bit is set in i:
print A[j]
print ‘\n’
Code
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int subsetSize = (int) Math.pow(2, n); // 1 << n
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < subsetSize; i++) {
List<Integer> single = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){
// if the mask and bit are set then
// we will include in the temp arr
// else we will not include
if((i & (1<<j)) > 0){
single.add(nums[j]);
}
}
ans.add(single);
}
return ans;
}
Dry running above code: Take for eg. n = 2, nums = { 10, 20}; We loop i 0 to 3, and j from 0 to nums.length.
i j 1 << j Set
00 0 01 []
00 1 10 [] -> added to Result
01 0 01 [10]
01 1 10 [10] -> added to Result
10 0 01 []
10 1 10 [20] -> added to Result
11 0 01 [10]
11 1 10 [10, 20] -> added to Result