Subtree Removal Game with Fibonacci Tree
Problem
A Fibonacci tree is a binary tree created using the order function order(n):
order(0)is the empty tree.order(1)is a binary tree with only one node.order(n)is a binary tree that consists of a root node with the left subtree asorder(n - 2)and the right subtree asorder(n - 1).
Alice and Bob are playing a game with a Fibonacci tree with Alice staring first. On each turn, a player selects a node and removes that node and its subtree. The player that is forced to delete root loses.
Given the integer n, return true if Alice wins the game or false if Bob wins, assuming both players play optimally.
A subtree of a binary tree tree is a tree that consists of a node in tree
and all of this node's descendants. The tree tree could also be considered as a subtree of itself.
Examples
Example 1:
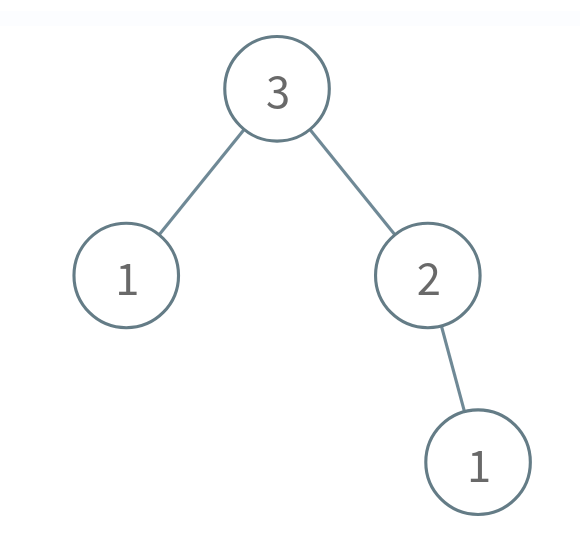
Input: n = 3
Output: true
Explanation:
Alice takes the node 1 in the right subtree.
Bob takes either the 1 in the left subtree or the 2 in the right subtree.
Alice takes whichever node Bob doesn't take.
Bob is forced to take the root node 3, so Bob will lose.
Return true because Alice wins.
Example 2:

Input: n = 1
Output: false
Explanation:
Alice is forced to take the root node 1, so Alice will lose.
Return false because Alice loses.
Example 3:
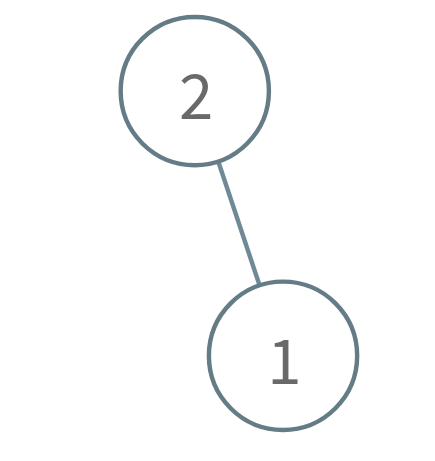
Input: n = 2
Output: true
Explanation:
Alice takes the node 1.
Bob is forced to take the root node 2, so Bob will lose.
Return true because Alice wins.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 100
Solution
Method 1 – Fibonacci Parity Game Analysis
Intuition
The game is played on a Fibonacci tree, where each subtree size follows the Fibonacci sequence. The winner is determined by the parity of n: if n is even, Alice can always win by taking the leftmost node; if n is odd, Bob will win because Alice is forced to take the root. This is due to the recursive structure and the way nodes are removed in each turn.
Approach
- If n == 1, Alice is forced to take the root and loses.
- If n == 2, Alice can take the only child and win.
- For n > 2, recursively check the parity of n:
- If n is even, Alice can always win.
- If n is odd, Bob will win.
- Return True if Alice wins, False otherwise.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool subtreeRemovalGame(int n) {
return n % 2 == 0;
}
};
Go
func subtreeRemovalGame(n int) bool {
return n%2 == 0
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean subtreeRemovalGame(int n) {
return n % 2 == 0;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun subtreeRemovalGame(n: Int): Boolean {
return n % 2 == 0
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def subtreeRemovalGame(self, n: int) -> bool:
return n % 2 == 0
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn subtree_removal_game(n: i32) -> bool {
n % 2 == 0
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
subtreeRemovalGame(n: number): boolean {
return n % 2 === 0;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(1)– Only a parity check is performed. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)– No extra space is used.