The Most Similar Path in a Graph
Problem
We have n cities and m bi-directional roads where roads[i] = [ai, bi]
connects city ai with city bi. Each city has a name consisting of exactly three upper-case English letters given in the string array names. Starting at any city x, you can reach any city y where y != x (i.e., the cities and the roads are forming an undirected connected graph).
You will be given a string array targetPath. You should find a path in the graph of the same length and with the minimum edit distance to
targetPath.
You need to return the order of the nodes in the path with the minimum edit distance. The path should be of the same length of targetPath and should be valid (i.e., there should be a direct road between ans[i] and ans[i + 1]).
If there are multiple answers return any one of them.
The edit distance is defined as follows:
define editDistance(targetPath, myPath) {
dis := 0
a := targetPath.length
b := myPath.length
if a != b {
return 1000000000
}
for (i:= 0; i < a; i += 1) {
if targetPath[i] != myPath[i] {
dis += 1
}
}
return dis
}
Examples
Example 1:
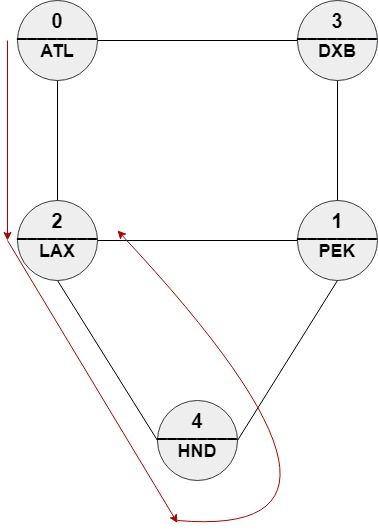
Input: n = 5, roads = [[0,2],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,4]], names = ["ATL","PEK","LAX","DXB","HND"], targetPath = ["ATL","DXB","HND","LAX"]
Output: [0,2,4,2]
Explanation: [0,2,4,2], [0,3,0,2] and [0,3,1,2] are accepted answers.
[0,2,4,2] is equivalent to ["ATL","LAX","HND","LAX"] which has edit distance = 1 with targetPath.
[0,3,0,2] is equivalent to ["ATL","DXB","ATL","LAX"] which has edit distance = 1 with targetPath.
[0,3,1,2] is equivalent to ["ATL","DXB","PEK","LAX"] which has edit distance = 1 with targetPath.
Example 2:
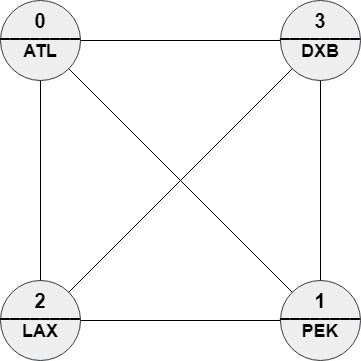
Input: n = 4, roads = [[1,0],[2,0],[3,0],[2,1],[3,1],[3,2]], names = ["ATL","PEK","LAX","DXB"], targetPath = ["ABC","DEF","GHI","JKL","MNO","PQR","STU","VWX"]
Output: [0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1]
Explanation: Any path in this graph has edit distance = 8 with targetPath.
Example 3:
**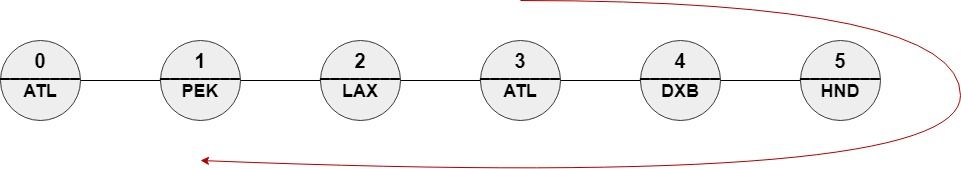**
Input: n = 6, roads = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5]], names = ["ATL","PEK","LAX","ATL","DXB","HND"], targetPath = ["ATL","DXB","HND","DXB","ATL","LAX","PEK"]
Output: [3,4,5,4,3,2,1]
Explanation: [3,4,5,4,3,2,1] is the only path with edit distance = 0 with targetPath.
It's equivalent to ["ATL","DXB","HND","DXB","ATL","LAX","PEK"]
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 100m == roads.lengthn - 1 <= m <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)0 <= ai, bi <= n - 1ai != bi- The graph is guaranteed to be connected and each pair of nodes may have at most one direct road.
names.length == nnames[i].length == 3names[i]consists of upper-case English letters.- There can be two cities with the same name.
1 <= targetPath.length <= 100targetPath[i].length == 3targetPath[i]consists of upper-case English letters.
Follow up: If each node can be visited only once in the path, What should you change in your solution?
Solution
Method 1 - Dynamic Programming on Graph (Backward DP)
Intuition
We use dynamic programming to find the path of minimum edit distance. For each position in the targetPath and each city, we keep the minimum edit distance to reach that city at that position, and a parent pointer to reconstruct the path. The backward DP (from last position to first) lets us compute costs using future states.
Approach
- Build an adjacency list for the graph.
- Initialize
dp(sizem x n) with large values andparentwith -1. - Set
dp[m-1][i] = 0ifnames[i] == targetPath[m-1]else1for all citiesi. - For
ifromm-2down to0, for each cityuand neighborvofu, updatedp[i][u]usingdp[i+1][v] + cost(u,i)wherecost(u,i)is0ifnames[u] == targetPath[i]else1. Store the chosenvinparent[i][u]. - Choose the start city with minimum
dp[0][city]and reconstruct the path using theparenttable.
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n * d)– For each of themtarget positions we consider up toncities and iterate over their neighbors (average degreed, worst-casen). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n)– We storedpandparenttables of sizem * n.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> mostSimilar(int n, vector<vector<int>>& roads, vector<string>& names, vector<string>& targetPath) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(n);
for (auto &r : roads) {
graph[r[0]].push_back(r[1]);
graph[r[1]].push_back(r[0]);
}
int m = targetPath.size();
const int INF = 1000000000;
vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, INF));
vector<vector<int>> parent(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
dp[m-1][i] = (names[i] == targetPath[m-1] ? 0 : 1);
for (int i = m-2; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int u = 0; u < n; ++u) {
for (int v : graph[u]) {
int cost = (names[u] == targetPath[i] ? 0 : 1) + dp[i+1][v];
if (cost < dp[i][u]) {
dp[i][u] = cost;
parent[i][u] = v;
}
}
}
}
int min_cost = INF, start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (dp[0][i] < min_cost) {
min_cost = dp[0][i];
start = i;
}
}
vector<int> path;
int u = start;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
path.push_back(u);
u = parent[i][u];
}
return path;
}
};
Go
package solution
func mostSimilar(n int, roads [][]int, names []string, targetPath []string) []int {
graph := make([][]int, n)
for _, r := range roads {
a, b := r[0], r[1]
graph[a] = append(graph[a], b)
graph[b] = append(graph[b], a)
}
m := len(targetPath)
const INF = 1000000000
dp := make([][]int, m)
parent := make([][]int, m)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, n)
parent[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
dp[i][j] = INF
parent[i][j] = -1
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if names[i] == targetPath[m-1] {
dp[m-1][i] = 0
} else {
dp[m-1][i] = 1
}
}
for i := m - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
for u := 0; u < n; u++ {
for _, v := range graph[u] {
cost := dp[i+1][v]
if names[u] != targetPath[i] {
cost += 1
}
if cost < dp[i][u] {
dp[i][u] = cost
parent[i][u] = v
}
}
}
}
minCost := INF
start := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if dp[0][i] < minCost {
minCost = dp[0][i]
start = i
}
}
path := make([]int, 0, m)
u := start
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
path = append(path, u)
u = parent[i][u]
}
return path
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> mostSimilar(int n, int[][] roads, List<String> names, List<String> targetPath) {
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] r : roads) {
graph.get(r[0]).add(r[1]);
graph.get(r[1]).add(r[0]);
}
int m = targetPath.size();
int INF = 1000000000;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
int[][] parent = new int[m][n];
for (int[] row : dp) Arrays.fill(row, INF);
for (int[] row : parent) Arrays.fill(row, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
dp[m-1][i] = names.get(i).equals(targetPath.get(m-1)) ? 0 : 1;
for (int i = m-2; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int u = 0; u < n; ++u) {
for (int v : graph.get(u)) {
int cost = (names.get(u).equals(targetPath.get(i)) ? 0 : 1) + dp[i+1][v];
if (cost < dp[i][u]) {
dp[i][u] = cost;
parent[i][u] = v;
}
}
}
}
int minCost = INF, start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (dp[0][i] < minCost) {
minCost = dp[0][i];
start = i;
}
}
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int u = start;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
path.add(u);
u = parent[i][u];
}
return path;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun mostSimilar(n: Int, roads: Array<IntArray>, names: List<String>, targetPath: List<String>): List<Int> {
val graph = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (r in roads) {
graph[r[0]].add(r[1])
graph[r[1]].add(r[0])
}
val m = targetPath.size
val INF = 1000000000
val dp = Array(m) { IntArray(n) { INF } }
val parent = Array(m) { IntArray(n) { -1 } }
for (i in 0 until n) dp[m-1][i] = if (names[i] == targetPath[m-1]) 0 else 1
for (i in m-2 downTo 0) {
for (u in 0 until n) {
for (v in graph[u]) {
var cost = dp[i+1][v]
if (names[u] != targetPath[i]) cost += 1
if (cost < dp[i][u]) {
dp[i][u] = cost
parent[i][u] = v
}
}
}
}
var minCost = INF
var start = 0
for (i in 0 until n) if (dp[0][i] < minCost) { minCost = dp[0][i]; start = i }
val path = ArrayList<Int>(m)
var u = start
for (i in 0 until m) {
path.add(u)
u = parent[i][u]
}
return path
}
}
Python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def mostSimilar(self, n: int, roads: List[List[int]], names: List[str], targetPath: List[str]) -> List[int]:
from collections import defaultdict
graph = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in roads:
graph[a].append(b)
graph[b].append(a)
m = len(targetPath)
INF = 10**9
dp = [[INF] * n for _ in range(m)]
parent = [[-1] * n for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(n):
dp[m-1][i] = 0 if names[i] == targetPath[m-1] else 1
for i in range(m-2, -1, -1):
for u in range(n):
for v in graph[u]:
cost = (0 if names[u] == targetPath[i] else 1) + dp[i+1][v]
if cost < dp[i][u]:
dp[i][u] = cost
parent[i][u] = v
min_cost, start = min((dp[0][i], i) for i in range(n))
path = []
u = start
for i in range(m):
path.append(u)
u = parent[i][u]
return path
Rust
use std::i32;
pub fn mostSimilar(n: i32, roads: Vec<Vec<i32>>, names: Vec<String>, target_path: Vec<String>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = n as usize;
let m = target_path.len();
let mut graph = vec![Vec::new(); n];
for r in &roads {
graph[r[0] as usize].push(r[1] as usize);
graph[r[1] as usize].push(r[0] as usize);
}
let mut dp = vec![vec![i32::MAX; n]; m];
let mut parent = vec![vec![-1; n]; m];
for i in 0..n {
dp[m-1][i] = if names[i] == target_path[m-1] { 0 } else { 1 };
}
for i in (0..m-1).rev() {
for u in 0..n {
for &v in &graph[u] {
let cost = (if names[u] == target_path[i] { 0 } else { 1 }) + dp[i+1][v];
if cost < dp[i][u] {
dp[i][u] = cost;
parent[i][u] = v as i32;
}
}
}
}
let (mut min_cost, mut start) = (i32::MAX, 0usize);
for i in 0..n {
if dp[0][i] < min_cost {
min_cost = dp[0][i];
start = i;
}
}
let mut path = Vec::with_capacity(m);
let mut u = start;
for i in 0..m {
path.push(u as i32);
u = parent[i][u] as usize;
}
path
}
TypeScript
function mostSimilar(n: number, roads: number[][], names: string[], targetPath: string[]): number[] {
const graph: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of roads) {
graph[a].push(b);
graph[b].push(a);
}
const m = targetPath.length;
const INF = 1e9;
const dp: number[][] = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(INF));
const parent: number[][] = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(-1));
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
dp[m-1][i] = names[i] === targetPath[m-1] ? 0 : 1;
}
for (let i = m-2; i >= 0; --i) {
for (let u = 0; u < n; ++u) {
for (const v of graph[u]) {
const cost = (names[u] === targetPath[i] ? 0 : 1) + dp[i+1][v];
if (cost < dp[i][u]) {
dp[i][u] = cost;
parent[i][u] = v;
}
}
}
}
let minCost = INF, start = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (dp[0][i] < minCost) {
minCost = dp[0][i];
start = i;
}
}
const path: number[] = [];
let u = start;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
path.push(u);
u = parent[i][u];
}
return path;
}