Transform to Chessboard
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given an n x n binary grid board. In each move, you can swap any two rows with each other, or any two columns with each other.
Return the minimum number of moves to transform the board into achessboard board. If the task is impossible, return -1.
A chessboard board is a board where no 0's and no 1's are 4-directionally adjacent.
Examples
Example 1
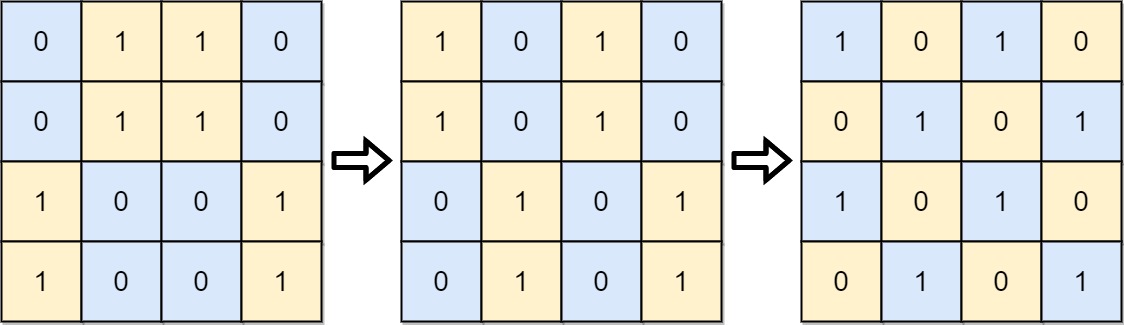
Input: board = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[1,0,0,1],[1,0,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation: One potential sequence of moves is shown.
The first move swaps the first and second column.
The second move swaps the second and third row.
Example 2
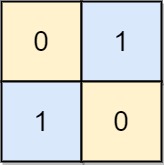
Input: board = [[0,1],[1,0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Also note that the board with 0 in the top left corner, is also a valid chessboard.
Example 3
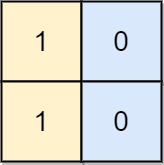
Input: board = [[1,0],[1,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: No matter what sequence of moves you make, you cannot end with a valid chessboard.
Constraints
n == board.lengthn == board[i].length2 <= n <= 30board[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
Method 1 – Pattern Analysis & Swaps
Intuition
To transform the board into a chessboard, all rows must be either the same as the first row or its inverse, and the same for columns. We count the number of swaps needed to arrange rows and columns into alternating patterns.
Approach
- Check if the board can be transformed: all rows (and columns) must be either the same as the first row (column) or its inverse.
- Count the number of 1s in the first row and first column. They must be either n//2 or (n+1)//2.
- For both rows and columns, count how many are out of place compared to the ideal chessboard pattern, and compute the minimum swaps needed.
Code
C++
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int movesToChessboard(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
int n = board.size();
int rowSum = 0, colSum = 0, rowSwap = 0, colSwap = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((board[0][0] ^ board[i][0] ^ board[0][j] ^ board[i][j]) != 0)
return -1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
rowSum += board[0][i];
colSum += board[i][0];
if (board[i][0] == i % 2) rowSwap++;
if (board[0][i] == i % 2) colSwap++;
}
if (rowSum != n/2 && rowSum != (n+1)/2) return -1;
if (colSum != n/2 && colSum != (n+1)/2) return -1;
if (n % 2) {
if (colSwap % 2) colSwap = n - colSwap;
if (rowSwap % 2) rowSwap = n - rowSwap;
} else {
colSwap = min(colSwap, n - colSwap);
rowSwap = min(rowSwap, n - rowSwap);
}
return (colSwap + rowSwap) / 2;
}
};
Java
class Solution {
public int movesToChessboard(int[][] board) {
int n = board.length;
int rowSum = 0, colSum = 0, rowSwap = 0, colSwap = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((board[0][0] ^ board[i][0] ^ board[0][j] ^ board[i][j]) != 0)
return -1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
rowSum += board[0][i];
colSum += board[i][0];
if (board[i][0] == i % 2) rowSwap++;
if (board[0][i] == i % 2) colSwap++;
}
if (rowSum != n/2 && rowSum != (n+1)/2) return -1;
if (colSum != n/2 && colSum != (n+1)/2) return -1;
if (n % 2 == 1) {
if (colSwap % 2 == 1) colSwap = n - colSwap;
if (rowSwap % 2 == 1) rowSwap = n - rowSwap;
} else {
colSwap = Math.min(colSwap, n - colSwap);
rowSwap = Math.min(rowSwap, n - rowSwap);
}
return (colSwap + rowSwap) / 2;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def movesToChessboard(self, board):
n = len(board)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if board[0][0] ^ board[i][0] ^ board[0][j] ^ board[i][j]:
return -1
rowSum = sum(board[0])
colSum = sum(board[i][0] for i in range(n))
rowSwap = sum(board[i][0] == i % 2 for i in range(n))
colSwap = sum(board[0][i] == i % 2 for i in range(n))
if not (n//2 <= rowSum <= (n+1)//2): return -1
if not (n//2 <= colSum <= (n+1)//2): return -1
if n % 2:
if colSwap % 2: colSwap = n - colSwap
if rowSwap % 2: rowSwap = n - rowSwap
else:
colSwap = min(colSwap, n - colSwap)
rowSwap = min(rowSwap, n - rowSwap)
return (colSwap + rowSwap) // 2
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn moves_to_chessboard(board: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = board.len();
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
if board[0][0] ^ board[i][0] ^ board[0][j] ^ board[i][j] != 0 {
return -1;
}
}
}
let row_sum: i32 = board[0].iter().sum();
let col_sum: i32 = (0..n).map(|i| board[i][0]).sum();
let row_swap: i32 = (0..n).map(|i| (board[i][0] == (i % 2) as i32) as i32).sum();
let col_swap: i32 = (0..n).map(|i| (board[0][i] == (i % 2) as i32) as i32).sum();
if row_sum != (n/2) as i32 && row_sum != ((n+1)/2) as i32 { return -1; }
if col_sum != (n/2) as i32 && col_sum != ((n+1)/2) as i32 { return -1; }
let mut row_swap = row_swap;
let mut col_swap = col_swap;
if n % 2 == 1 {
if col_swap % 2 == 1 { col_swap = n as i32 - col_swap; }
if row_swap % 2 == 1 { row_swap = n as i32 - row_swap; }
} else {
col_swap = col_swap.min(n as i32 - col_swap);
row_swap = row_swap.min(n as i32 - row_swap);
}
(col_swap + row_swap) / 2
}
}
TypeScript
function movesToChessboard(board: number[][]): number {
const n = board.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((board[0][0] ^ board[i][0] ^ board[0][j] ^ board[i][j]) !== 0) return -1;
}
}
let rowSum = 0, colSum = 0, rowSwap = 0, colSwap = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
rowSum += board[0][i];
colSum += board[i][0];
if (board[i][0] === i % 2) rowSwap++;
if (board[0][i] === i % 2) colSwap++;
}
if (rowSum !== Math.floor(n/2) && rowSum !== Math.floor((n+1)/2)) return -1;
if (colSum !== Math.floor(n/2) && colSum !== Math.floor((n+1)/2)) return -1;
if (n % 2) {
if (colSwap % 2) colSwap = n - colSwap;
if (rowSwap % 2) rowSwap = n - rowSwap;
} else {
colSwap = Math.min(colSwap, n - colSwap);
rowSwap = Math.min(rowSwap, n - rowSwap);
}
return Math.floor((colSwap + rowSwap) / 2);
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)