Tree of Coprimes
Problem
There is a tree (i.e., a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1
edges. Each node has a value associated with it, and the root of the tree is node 0.
To represent this tree, you are given an integer array nums and a 2D array
edges. Each nums[i] represents the ith node's value, and each edges[j] = [uj, vj] represents an edge between nodes uj and vj in the tree.
Two values x and y are coprime if gcd(x, y) == 1 where gcd(x, y)
is the greatest common divisor of x and y.
An ancestor of a node i is any other node on the shortest path from node i
to the root. A node is not considered an ancestor of itself.
Return an arrayans of sizen, whereans[i]is the closest ancestor to nodei such thatnums[i] andnums[ans[i]] are coprime , or -1
if there is no such ancestor.
Examples
Example 1
**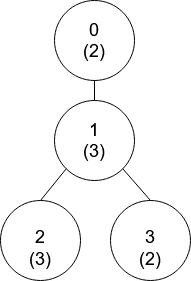**
Input: nums = [2,3,3,2], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: [-1,0,0,1]
Explanation: In the above figure, each node's value is in parentheses.
- Node 0 has no coprime ancestors.
- Node 1 has only one ancestor, node 0. Their values are coprime (gcd(2,3) == 1).
- Node 2 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. Node 1's value is not coprime (gcd(3,3) == 3), but node 0's
value is (gcd(2,3) == 1), so node 0 is the closest valid ancestor.
- Node 3 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. It is coprime with node 1 (gcd(3,2) == 1), so node 1 is its
closest valid ancestor.
Example 2
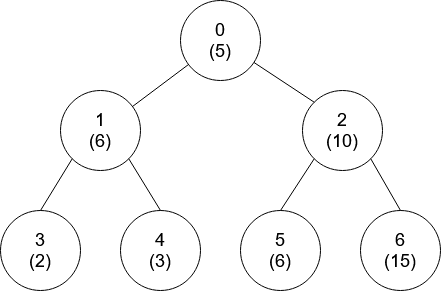
Input: nums = [5,6,10,2,3,6,15], edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
Output: [-1,0,-1,0,0,0,-1]
Constraints
nums.length == n1 <= nums[i] <= 501 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[j].length == 20 <= uj, vj < nuj != vj
Solution
Method 1 – DFS with Ancestor Tracking
Intuition
For each node, keep track of the most recent ancestor for each possible value (1..50). For each node, check all possible values for coprimality and pick the closest ancestor.
Approach
- Build the tree as an adjacency list.
- Use DFS, passing down a map of the latest ancestor for each value.
- For each node, check all values 1..50 for coprimality with nums[node].
- For each child, update the ancestor map and recurse.
Code
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] getCoprimes(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
int n = nums.length;
List<Integer>[] g = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
g[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
int[] last = new int[51];
int[] depth = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(last, -1);
dfs(0, -1, 0, nums, g, ans, last, depth);
return ans;
}
void dfs(int u, int p, int d, int[] nums, List<Integer>[] g, int[] ans, int[] last, int[] depth) {
int maxDepth = -1, ancestor = -1;
for (int v = 1; v <= 50; ++v) {
if (gcd(nums[u], v) == 1 && last[v] != -1 && depth[last[v]] > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth[last[v]];
ancestor = last[v];
}
}
ans[u] = ancestor;
int prev = last[nums[u]];
last[nums[u]] = u;
depth[u] = d;
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (v != p) dfs(v, u, d+1, nums, g, ans, last, depth);
}
last[nums[u]] = prev;
}
int gcd(int a, int b) { return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); }
}
Python
def getCoprimes(nums, edges):
from math import gcd
n = len(nums)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
ans = [-1]*n
last = [-1]*51
depth = [0]*n
def dfs(u, p, d):
maxd, ancestor = -1, -1
for v in range(1, 51):
if gcd(nums[u], v) == 1 and last[v] != -1 and depth[last[v]] > maxd:
maxd = depth[last[v]]
ancestor = last[v]
ans[u] = ancestor
prev = last[nums[u]]
last[nums[u]] = u
depth[u] = d
for v in g[u]:
if v != p:
dfs(v, u, d+1)
last[nums[u]] = prev
dfs(0, -1, 0)
return ans
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n * 50)— For each node, check up to 50 possible values. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n + 50)— For tree and ancestor tracking.