Two Sum BSTs
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given the roots of two binary search trees, root1 and root2, return true
if and only if there is a node in the first tree and a node in the second tree whose values sum up to a given integer target.
Examples
Example 1:
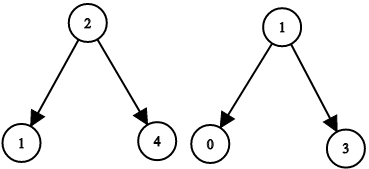
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3], target = 5
Output: true
Explanation: 2 and 3 sum up to 5.
Example 2:
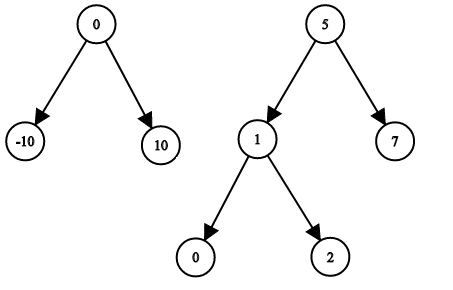
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2], target = 18
Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. -10^9 <= Node.val, target <= 10^9
Solution
Method 1 – Hash Set or Inorder Traversal
Intuition
Store all values from one tree in a set, then for each node in the other tree, check if target - node.val exists in the set.
Approach
- Traverse root1 and store all values in a set.
- Traverse root2 and for each node, check if target - node.val is in the set.
- Return true if found, else false.
Code
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public boolean twoSumBSTs(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2, int target) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
fill(root1, set);
return find(root2, set, target);
}
void fill(TreeNode node, Set<Integer> set) {
if (node == null) return;
set.add(node.val);
fill(node.left, set);
fill(node.right, set);
}
boolean find(TreeNode node, Set<Integer> set, int target) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (set.contains(target - node.val)) return true;
return find(node.left, set, target) || find(node.right, set, target);
}
}
Python
def twoSumBSTs(root1, root2, target):
def fill(node, s):
if not node: return
s.add(node.val)
fill(node.left, s)
fill(node.right, s)
s = set()
fill(root1, s)
def find(node):
if not node: return False
if target - node.val in s: return True
return find(node.left) or find(node.right)
return find(root2)
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n + m)— n, m = number of nodes in each tree. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)— For the set of values from one tree.