Unique Paths in Grid 1-2 - Get all paths moving right or down
Problem
There is a robot on an m x n grid. The robot is initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m - 1][n - 1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Given the two integers m and n, return all possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
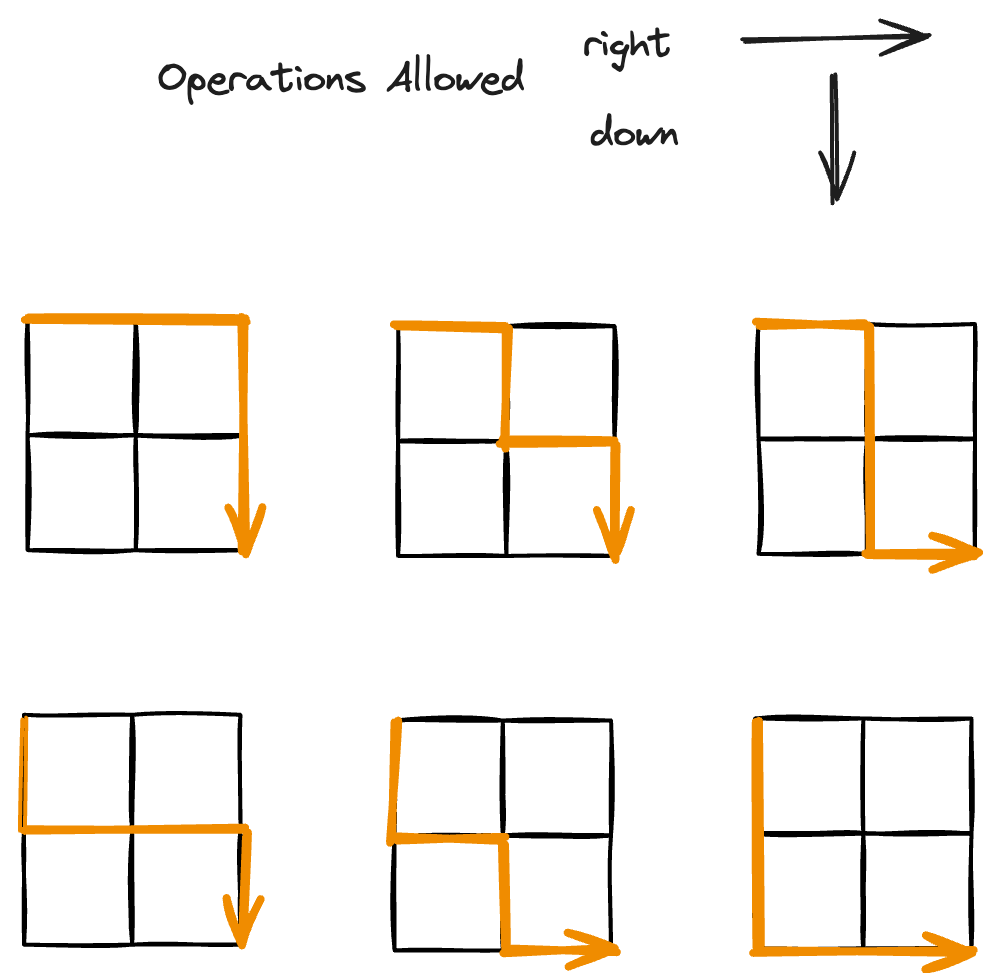
Examples
Example 1:
Input : m = 2, n = 2
Output : [
[[0, 0], [0,1], [1,1]],
[[0, 0], [1, 0], [1,1]]
2 possible routes : (0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (1, 1)
Follow up
Imagine certain squares are “off limits”, such that the robot can not step on them. Design an algorithm to get all possible paths for the robot.
Refer [Unique Paths in Grid - Get all paths moving right or down with obstacles](unique-paths-in-grid-get-all-paths-moving-right-or-down-with-obstacles)
Solution
Method 1 - Backtracking
We solved the similar question - [Unique Paths in Grid 1 - Count all paths moving right or down](unique-paths-in-grid-1-count-all-paths-moving-right-or-down), where we had to find the count of number of paths. Here we have to print the paths.
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public List < List<int[] >> findAllPaths(int m, int n) {
List <List<int[]>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
List <int[]> currentPath = new ArrayList<>();
currentPath.add(new int[] {
0, 0
});
backtrack(m, n, 0, 0, currentPath, paths);
return paths;
}
private void backtrack(int m, int n, int row, int col, List <int[]> currentPath, List <List<int[]>> paths) {
if (row == m - 1 && col == n - 1) {
paths.add(new ArrayList<>(currentPath)); // Add a copy of the currentPath
return;
}
// Move Down
if (row < m - 1) {
currentPath.add(new int[] {
row + 1, col
}); // Move down
backtrack(m, n, row + 1, col, currentPath, paths);
currentPath.remove(currentPath.size() - 1); // Backtrack
}
// Move Right
if (col < n - 1) {
currentPath.add(new int[] {
row, col + 1
}); // Move right
backtrack(m, n, row, col + 1, currentPath, paths);
currentPath.remove(currentPath.size() - 1); // Backtrack
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
List < List<int[] >> paths = solution.findAllPaths(2, 3);
// Print all paths
for (List < int[] > path: paths) {
System.out.print("[ ");
for (int[] step: path) {
System.out.print("[" + step[0] + "," + step[1] + "] ");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(2 ^ (m+n)) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m + n)for recursive stack