Unique Paths in Grid 2 - Count all paths moving right or down with obstacles
Problem
You are given an m x n integer array grid. There is a robot initially located at the top-left corner (i.e., grid[0][0]). The robot tries to move to the bottom-right corner (i.e., grid[m-1][n-1]). The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time.
An obstacle and space are marked as 1 or 0 respectively in grid. A path that the robot takes cannot include any square that is an obstacle.
Return the number of possible unique paths that the robot can take to reach the bottom-right corner.
The testcases are generated so that the answer will be less than or equal to 2 * 10^9.
Examples
Example 1:
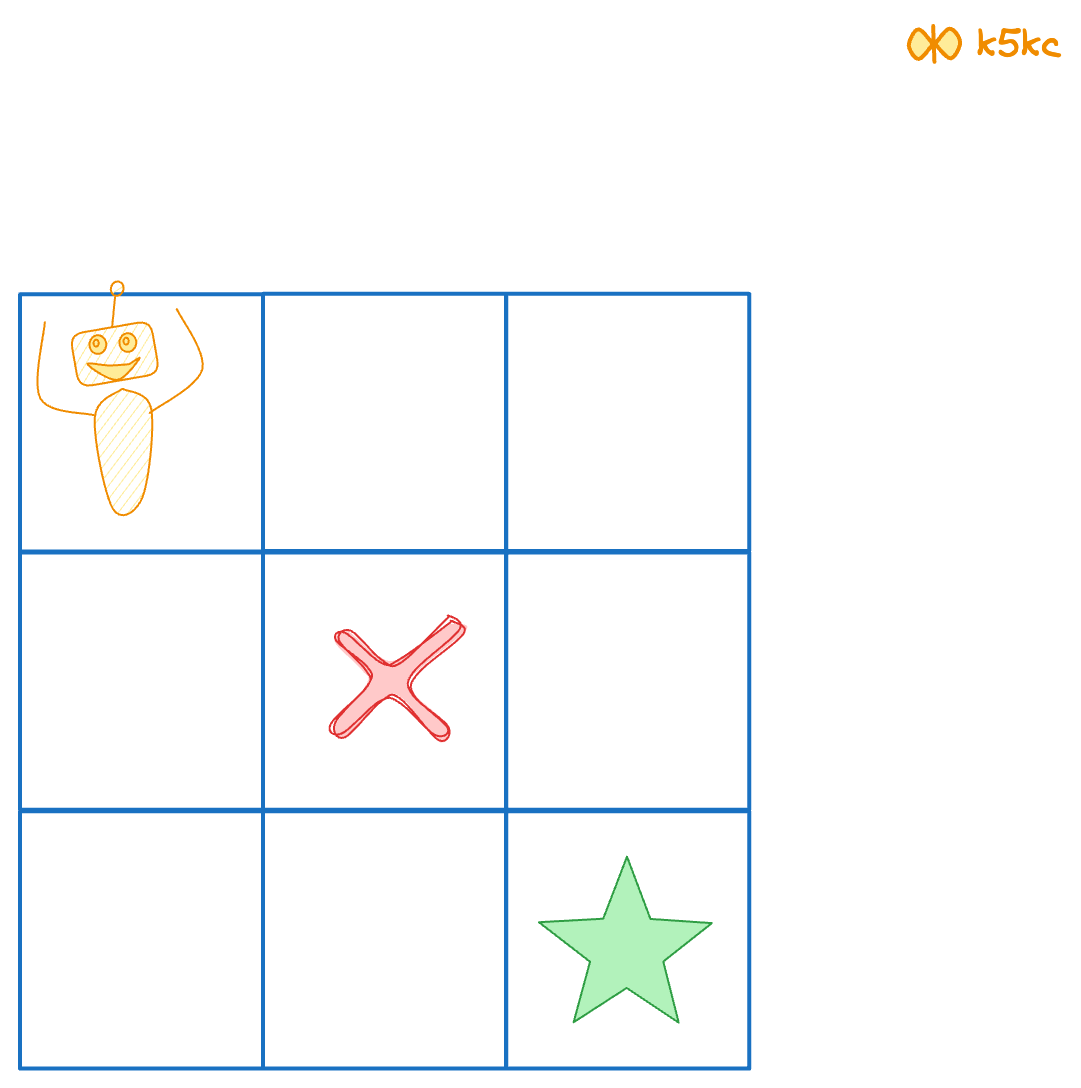
There is one obstacle in the middle of a 3x3 grid as illustrated below.
Input: obstacleGrid =[[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 2
Explanation: There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: obstacleGrid =[[0,1],[0,0]]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: obstacleGrid =[[0,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,1,0]]
Output: 3
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
This is follow up of [Unique Paths in Grid 1 - Count all paths moving right or down](unique-paths-in-grid-1-count-all-paths-moving-right-or-down).
Solution
Method 1 - Recursion
Recursion is straightforward. Starting from (0, 0), we attempt to move right or down unless an obstacle or boundary is encountered. If the destination is reached, count it as one unique path.
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
return dfs(obstacleGrid, 0, 0, m, n);
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j, int m, int n) {
if (i >= m || j >= n || grid[i][j] == 1) { // Out of bounds or obstacle
return 0;
}
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) { // Reached destination
return 1;
}
return dfs(grid, i + 1, j, m, n) + dfs(grid, i, j + 1, m, n); // Move down or right
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(2^(m+n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m+n)
Method 2 - Top Down DP
For top-down DP, we introduce a memo array to remember results of subproblems to avoid recalculating them. At each cell (i, j), we calculate the number of paths recursively and store the result in memo[i][j]. If we've already computed the number of paths from that cell, we just return the stored value.
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
return dfs(obstacleGrid, 0, 0, m, n, new Integer[m][n]);
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j, int m, int n, Integer[][] memo) {
if (i >= m || j >= n || grid[i][j] == 1) { // Out of bounds or obstacle
return 0;
}
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) { // Reached destination
return 1;
}
if (memo[i][j] != null) {
return memo[i][j];
}
return memo[i][j] = dfs(grid, i + 1, j, m, n, memo) + dfs(grid, i, j + 1, m, n, memo); // Move down or right
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m*n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m*n)
Method 3 - Bottom up DP
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
// If starting cell has an obstacle, there is no path.
if (obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) {
return 0;
}
// Initialize starting cell
dp[0][0] = 1;
// Fill out the first column
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
if (obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0 && dp[i - 1][0] == 1) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
}
// Fill out the first row
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0 && dp[0][j - 1] == 1) {
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
}
// Iterate through grid and populate number of paths for each cell
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1]; // Bottom-right corner has the final count
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m*n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m*n)
Method 4 - Space Optimized DP with linear space
This is a typical 2D DP problem, we can store value in 2D DP array, but since we only need to use value at dp[i - 1][j] and dp[i][j - 1] to update dp[i][j], we don't need to store the whole 2D table, but instead store value in an 1D array, and update data by using dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1], (where here dp[j] corresponding to the dp[i - 1][j]) and dp[j - 1] corresponding to the dp[i][j - 1] in the 2D array)
Code
Java
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid[0].length; // m for the number of columns
int[] dp = new int[m];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int[] row: obstacleGrid) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (row[j] == 1) {
dp[j] = 0;
} else if (j > 0) {
dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
}
}
}
return dp[m - 1];
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m*n) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m)
Method 5 - Constant space DP with matrix modification
Can We Save More Space? Yes, Make it O(1) by Modifying Matrix
Code
Java
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
//Empty case
if (obstacleGrid.length == 0) return 0;
int rows = obstacleGrid.length;
int cols = obstacleGrid[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1)
obstacleGrid[i][j] = 0;
else if (i == 0 && j == 0)
obstacleGrid[i][j] = 1;
else if (i == 0)
obstacleGrid[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i][j - 1]; // For row 0, if there are no paths to left cell, then its 0,else 1
else if (j == 0)
obstacleGrid[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i - 1][j]; // For col 0, if there are no paths to upper cell, then its 0,else 1
else
obstacleGrid[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i - 1][j] + obstacleGrid[i][j - 1];
}
}
return obstacleGrid[rows - 1][cols - 1];
}
}