Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Preorder Traversal
Problem
Given two integer arrays preorder and inorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree and inorder is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Examples
Example 1:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Solution
Video explanation
Here is the video explaining this method in detail. Please check it out:
<div class="youtube-embed"><iframe src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/v2Nhmp3YU1U" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></div>
Method 1 - Recursive Divide and Conquer
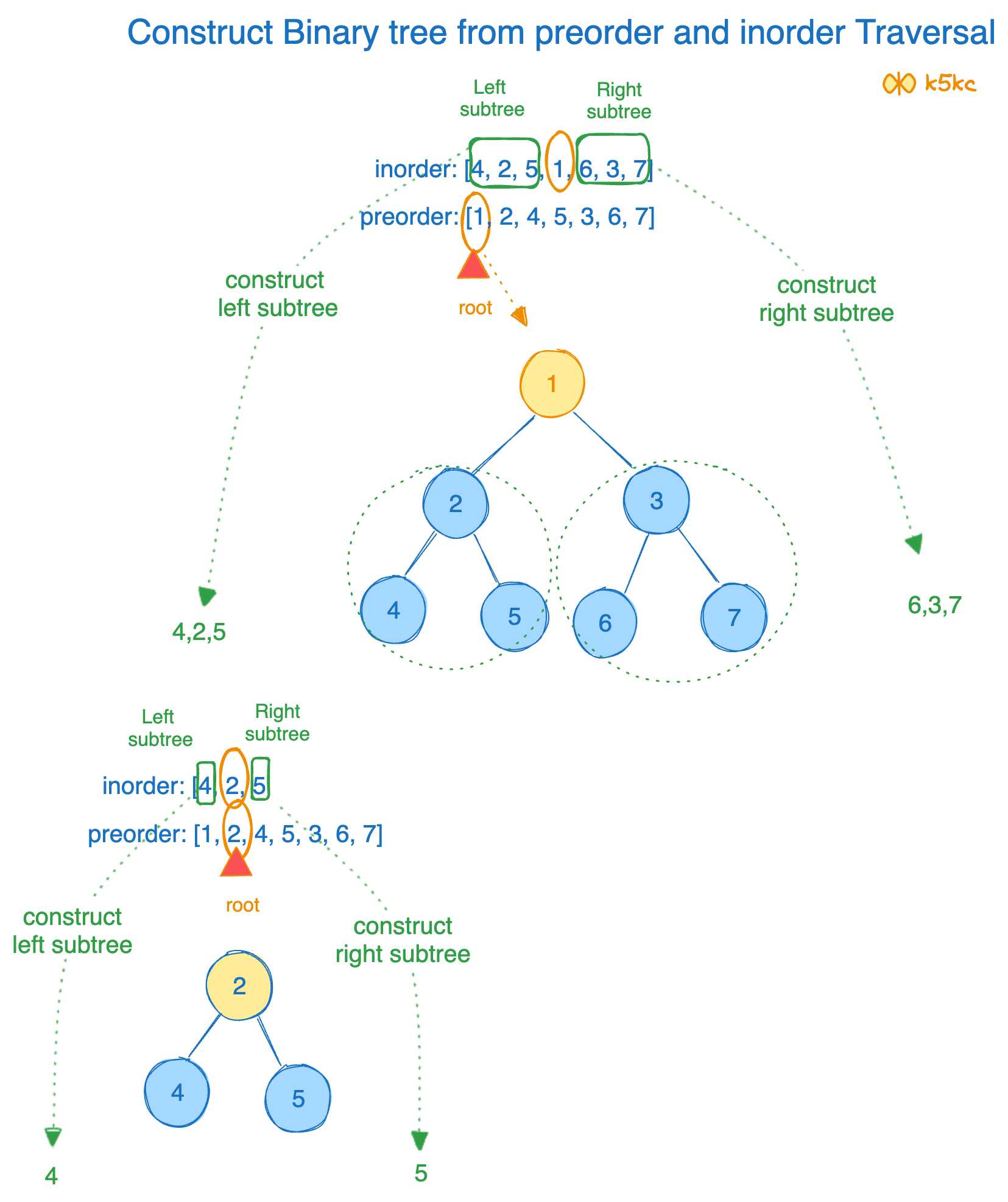
Lets look at the binary tree:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
The inorder and preorder traversal are:
inorder = [4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7]
preorder = [1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7]
How does preorder[] array helps?
The first element in preorder[] acts as the root of the tree (in this case, 1).
How does inorder[] array helps?
inorder[] helps determine the left and right subtrees of the root. Elements appearing before the root in inorder[] belong to the left subtree, while elements appearing after belong to the right subtree. In our case, it is [4, 2, 5] on left and [6, 3, 7] on right. (See picture below).
See this step above and recursively construct left subtree and link it root.left and recursively construct right subtree and link it root.right.
Code
Java
class Solution {
private int[] preorder;
private int[] inorder;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if (preorder == null || preorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0 || preLength != inLength) {
return null;
}
// We use indices to pass subarrays, which is more efficient than copying arrays on each call.
this.preorder = preorder;
this.inorder = inorder;
int preLength = preorder.length;
int inLength = inorder.length;
return helper(preorder, inorder, 0, 0, inLength - 1);
}
private TreeNode helper(int preStart, int inStart, int inEnd) {
if (inStart > inEnd || preStart > preorder.length - 1) {
return null;
}
// Pick current node from Preorder traversal using preStart and increment preStart
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preStart]);
// If this node has no children then return
if (inStart == inEnd) {
return root;
}
// Else find the index of this node in Inorder traversal
int inIndex = linearSearch(inorder, root.val, inStart, inEnd);
// Using index in Inorder traversal, construct left and right subtrees
root.left = helper(preStart + 1, inStart, inIndex - 1);
// We are skipping the elements on the left of the current pre order node by adding inIndex - inStart + 1
root.right = helper(preStart + inIndex - inStart + 1, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int value, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (arr[i] == value) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not preorder or not inorder:
return None
root_val = preorder[0]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
# This O(n) scan is the bottleneck
inorder_root_index = inorder.index(root_val)
# List slicing is inefficient for each recursive call
left_inorder = inorder[:inorder_root_index]
right_inorder = inorder[inorder_root_index + 1:]
left_preorder = preorder[1:1 + len(left_inorder)]
right_preorder = preorder[1 + len(left_inorder):]
root.left = self.buildTree(left_preorder, left_inorder)
root.right = self.buildTree(right_preorder, right_inorder)
return root
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2)in the implementation shown above that useslinearSearchto locate the root in the inorder array. In the worst case (skewed trees), each recursive step performs an O(n) scan which leads to a quadratic total cost.- Optimized variant:
O(n)if you precompute a hash map from value → inorder index before recursion; then each node is created and positioned in O(1) work.
- Optimized variant:
- 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)total. The output tree storesnnodes; recursion stack uses O(h) auxiliary space wherehis the tree height (worst-case O(n) for a skewed tree). The optimized variant additionally requires O(n) space for the index map.
Method 2 - Recursive Divide and Conquer with Inorder Index Mapping
Intuition
The naive approach has two main bottlenecks: the O(n) linear scan to find the root in the inorder array, and (in some implementations) the O(k) cost of slicing arrays at each step. We can eliminate both.
- The problem states that all values are unique. This is the key that allows us to use a hash map to store the indices of the
inorderelements, turning ourO(n)search into anO(1)lookup. - To eliminate the slicing cost, we use indices to define the boundaries of our current subproblem for both arrays, ensuring we don't create new arrays in memory.
Approach
- First, make a single pass through the
inorderarray to build a hash map (inorder_map) that maps each element's value to its index. - Create a recursive helper function that takes indices as arguments (
preStart,inStart,inEnd) to define the current subproblem. - In the helper, the current
rootispreorder[preStart]. - Use the
inorder_mapto find the root's index (inIndex) inO(1)time. - Calculate the size of the left subtree:
leftSubtreeSize = inIndex - inStart. - Make two recursive calls, calculating the new index boundaries for each:
- Left child: The
preorderstarts atpreStart + 1, and theinordersegment is frominStarttoinIndex - 1. - Right child: The
preorderstarts atpreStart + 1 + leftSubtreeSize, and theinordersegment is frominIndex + 1toinEnd.
- Left child: The
- This approach processes each node once with
O(1)work for the lookup, resulting in an optimalO(n)time complexity.
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n). For each node inpreorderfinding its index ininordernow just takesO(n)time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)for recursion stack and hashmap to store inorder indices.
Code
Java
class Solution {
private int[] preorder;
private Map<Integer, Integer> inorderMap;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
this.inorderMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
this.inorderMap.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return helper(0, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode helper(int preStart, int inStart, int inEnd) {
// Base case
if (inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
// The root is the first element in the current preorder segment
int rootVal = this.preorder[preStart];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// Find root's index in O(1) using the map
int inIndex = this.inorderMap.get(rootVal);
// Calculate the size of the left subtree
int leftSubtreeSize = inIndex - inStart;
// Recursive calls are now identical in structure to the naive version
root.left = helper(preStart + 1, inStart, inIndex - 1);
root.right = helper(preStart + 1 + leftSubtreeSize, inIndex + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
self.preorder = preorder
self.inorder_map = {val: i for i, val in enumerate(inorder)}
return self.build_helper(0, 0, len(inorder) - 1)
def build_helper(self, pre_start: int, in_start: int, in_end: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
# Base case
if in_start > in_end:
return None
# The root is the first element in the current preorder segment
root_val = self.preorder[pre_start]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
# Find root's index in O(1) using the map
in_index = self.inorder_map[root_val]
# Calculate the size of the left subtree
left_subtree_size = in_index - in_start
# Recursive calls are now identical in structure to the naive version
root.left = self.build_helper(pre_start + 1, in_start, in_index - 1)
root.right = self.build_helper(pre_start + 1 + left_subtree_size, in_index + 1, in_end)
return root